Cuba is a realm of enchantment and mystery, an island nation teeming with history, culture, and natural splendor. It is located at the northwestern periphery of the Caribbean Sea at the confluence of the Gulf of Mexico and the North Atlantic Ocean. The country includes the island of Cuba and over 4,000 surrounding islands and islets. The main island is the westernmost of the Greater Antilles archipelago and the West Indies (of which the Greater Antilles is a part) and the largest island in the Caribbean. It measures over 700 miles from its easternmost to its westernmost point and roughly 100 miles north-to-south at its widest.
The majority of Cuba’s interior landscape consists of flat and rolling plains, with gentle hills rising above the landscape in its west and southern-central regions. The island’s one notable mountain range, the Sierra Maestra, anchors its southeastern extremity.
Cuba experiences a tropical climate with moderate temperatures throughout the year. The highest summer daytime temperatures reach the low 90s (Fahrenheit) and winter sees nighttime lows as cool as the mid 60s. It has a distinct rainy season spanning from May to October and a dry period from November to April. Cuba is located along a corridor that hurricanes frequently traverse and have historically impacted the area in September and October.
Cuba is renowned for its variegated culture. The Ciboney, Guanahatabey, and Taíno people are its earliest known inhabitants. Italian explorer Christopher Columbus landed on the shores of the island in late October of 1492, naming it “Isla Juana.” Spain quickly colonized the area, eventually naming it Cuba. Cities, towns, and agriculture developed in the ensuing years, and the country experienced a series of wars and tumultuous political upheavals. The Cuban Revolution of 1953-1959 is one of modern history’s most notable and culminated in the government that rules the country to this day. Culturally, the nation is composed of people with Caribbean native, African, and European descent. Today, Cuba is a vibrant land of colonial towns and cities set amid tapestries of natural beauty and agricultural expanses.
This bush trip explores all the wonders that Cuba has to offer, including its coasts, inland plains and uplands, and villages, towns, and cities. It begins on its southeastern extremity and traverses the island’s midsection and southern coastline before drawing to a close at its fabled capital, Havana.
Total Legs: 7 Total Distance: 556 Total Time(125kts): 4 hours 26 minutes
Leg 1
Ap. Internaz. Antonio Maceo to Frank País
Leg Distance: 85.23 Approximate time at 125kts: 41 minutes.
Ap. Internaz. Antonio Maceo(MUCU) to Santiago de Cuba(POI1)
Distance: 3.52NM Bearing: 9° 2 minutes
After lifting off from Antonio Maceo Airport, set a course to the north, flying away from the Caribbean coastline of southeastern Cuba. Gain a visual on Santiago de Cuba Bay (Bahía de Santiago de Cuba) and follow its eastern shoreline to the city of Santiago de Cuba. Santiago de Cuba, the second largest city in the nation by population, is one of Cuba’s most historically significant cities. It was the capital of the Spanish colony of Cuba from 1522 to 1589 and is today the capital of the Santiago de Cuba Province. In 1898, the city was the location of the most devastating blow to Spain during the Spanish-American War, near San Juan Hill. Santiago de Cuba is today an important Caribbean port city and is renowned for its variety of beautiful architecture, notably of Baroque, neoclassical, and Renaissance styles.

Santiago de Cuba(POI1) to Gota Blanca Reservoir(POI2)
Distance: 13.12NM Bearing: 310° 6 minutes
Turn onto a northwest course over Santiago de Cuba and sight the Parada Reservoir (Embalse Parada) and the large earthen dam on its southern end. Fly just to the north of the reservoir and then sight the village of El Cobre. El Cobre is a town that developed around the Cobre mine, an open pit copper mine that the Spaniards opened in 1544. The mine, the first mine of its type established in Cuba, operated until 1998. Pass to the north of El Cobre and then gain a visual on the Gota Blanca Reservoir. Pass over the reservoir where its western and southeastern branches meet its main branch.

Gota Blanca Reservoir(POI2) to Carlos Manuel de Céspedes Reservoir(POI3)
Distance: 11.71NM Bearing: 304° 6 minutes
Maintain heading and pass over the low peaks on the northeastern extent of the Sierra Maestra. The Sierra Maestra, Cuba’s most notable mountain range, rises abruptly from the Caribbean Sea along Cuba’s southeastern coastline. The highest point of the range, and all of Cuba, is Pico Turquino, which stands 6,476 feet above sea level. Continue on course and pass over the midline of the Carlos Manuel de Céspedes Reservoir (Embalse Carlos Manuel de Céspedes).

Carlos Manuel de Céspedes Reservoir(POI3) to Jiguaní(POI4)
Distance: 14.38NM Bearing: 315° 7 minutes
Pass over the western arm of the Carlos Manuel de Céspedes Reservoir and gain a visual in the distance of Carretera Central de Cuba (Central Highway of Cuba). Merge with the pathway of the highway and a rail line at the village of Baire and follow both to the city of Jiguaní.
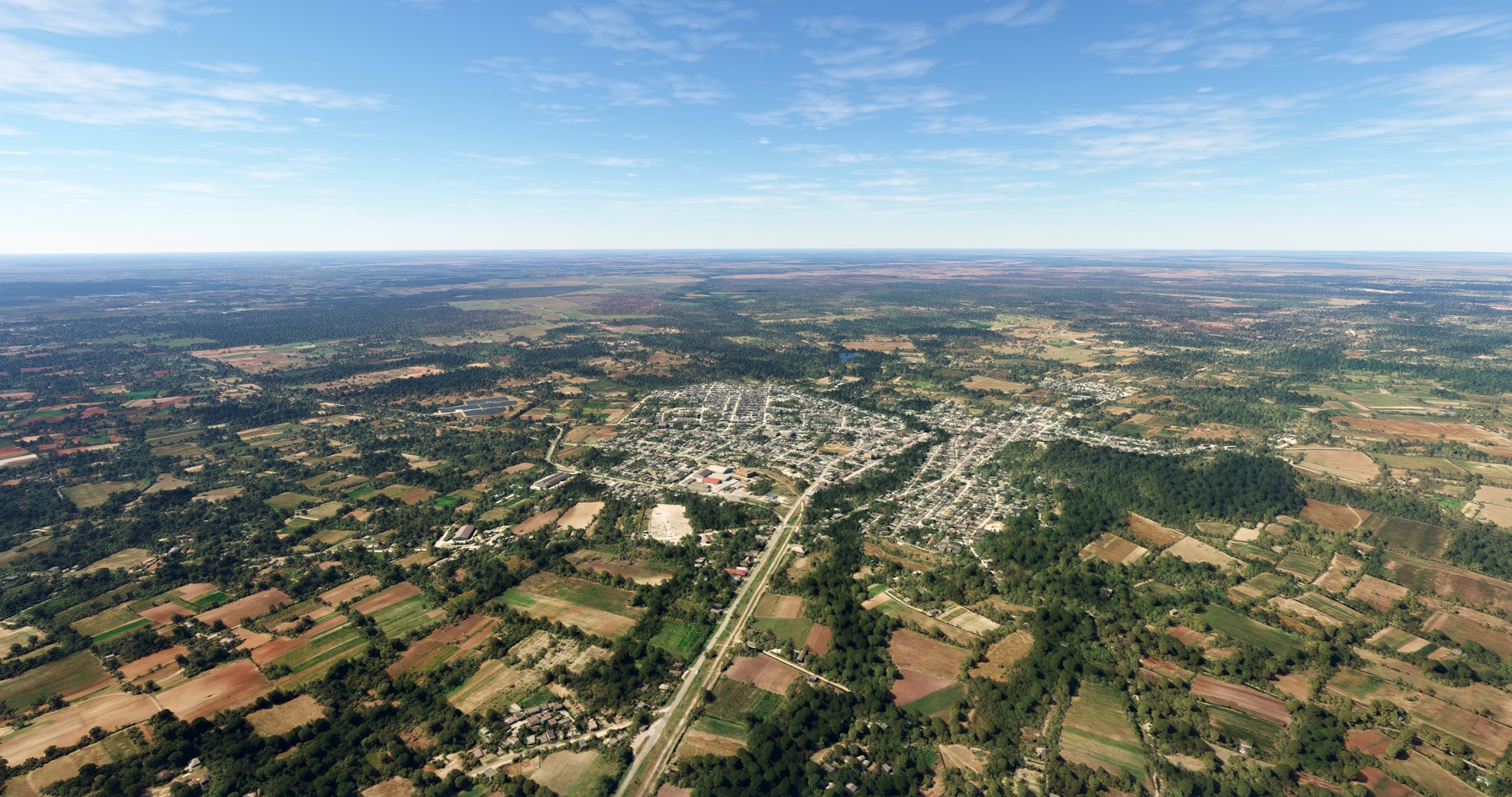
Jiguaní(POI4) to Bayamo(POI5)
Distance: 11.93NM Bearing: 283° 6 minutes
At Jiguaní, turn onto a due west course and parallel the pathway of the Carretera Central, remaining to its north. Continue on course to the city of Bayamo, the capital of the Granma Province. Bayamo was founded in 1513 and is one of the oldest population centers in Cuba and all the Western Hemisphere.

Bayamo(POI5) to Cauto Cristo(POI6)
Distance: 14.15NM Bearing: 50° 7 minutes
Turn onto a northeast heading over Bayamo and parallel Carretera Central de Cuba to the village of Cauto Cristo, which lies on the Cauto River. The Cauto River, or Río Cauto, originates in the Sierra Maestra and runs for 231 miles to the Caribbean Sea at the port city of Manzanillo, in southern Cuba.

Cauto Cristo(POI6) to Frank País(MUHG)
Distance: 16.42NM Bearing: 42° 8 minutes
Continue on course, following the Carretera Central, and land at Frank País Airport, which serves the city of Holguín. The airport is historically significant in Cuba as it was one of the stops on the nation’s first airmail route, which ran from Havana to Santiago de Cuba.

Leg 2
Frank País to Ap. Internaz. Ignacio Agramonte
Leg Distance: 108.12 Approximate time at 125kts: 52 minutes.
Frank País(MUHG) to Holguín(POI7)
Distance: 6.47NM Bearing: 36° 3 minutes
Lift off from Frank País Airport and set a course to the northeast, following the Carretera Central to the city of Holguín. Holguín, which was founded in 1523, is Cuba’s fourth largest city.

Holguín(POI7) to Las Calabazas(POI8)
Distance: 15.04NM Bearing: 274° 7 minutes
Over Holguín, turn on to a course to the west, and follow the Central Highway past the villages of Cruce San Andrés and Cruce de Maceo to reach the small town of Las Calabazas.

Las Calabazas(POI8) to Buenaventura(POI9)
Distance: 6.2NM Bearing: 282° 3 minutes
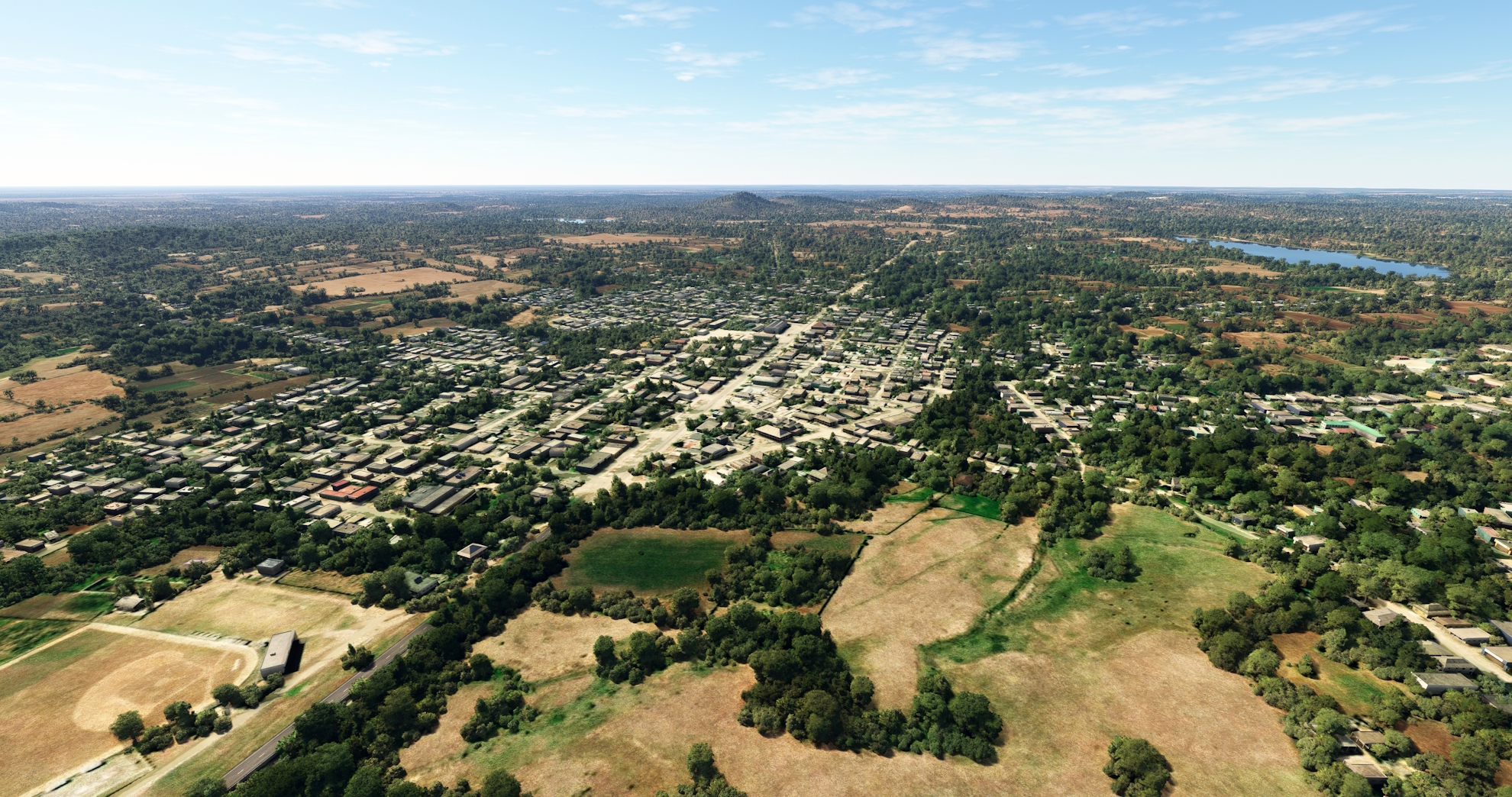
Continue following the highway to the town of Buenaventura, the seat of the municipality of Calixto García.
Buenaventura(POI9) to Limones Reservoir(POI10)
Distance: 13.94NM Bearing: 281° 7 minutes
Continue on a westerly course after passing over Buenaventura, remaining to the south of the Carretera Central. Sight and fly over the small Limones Reservoir (Embalse Limones).

Limones Reservoir(POI10) to Las Tunas(POI11)
Distance: 6.31NM Bearing: 334° 3 minutes
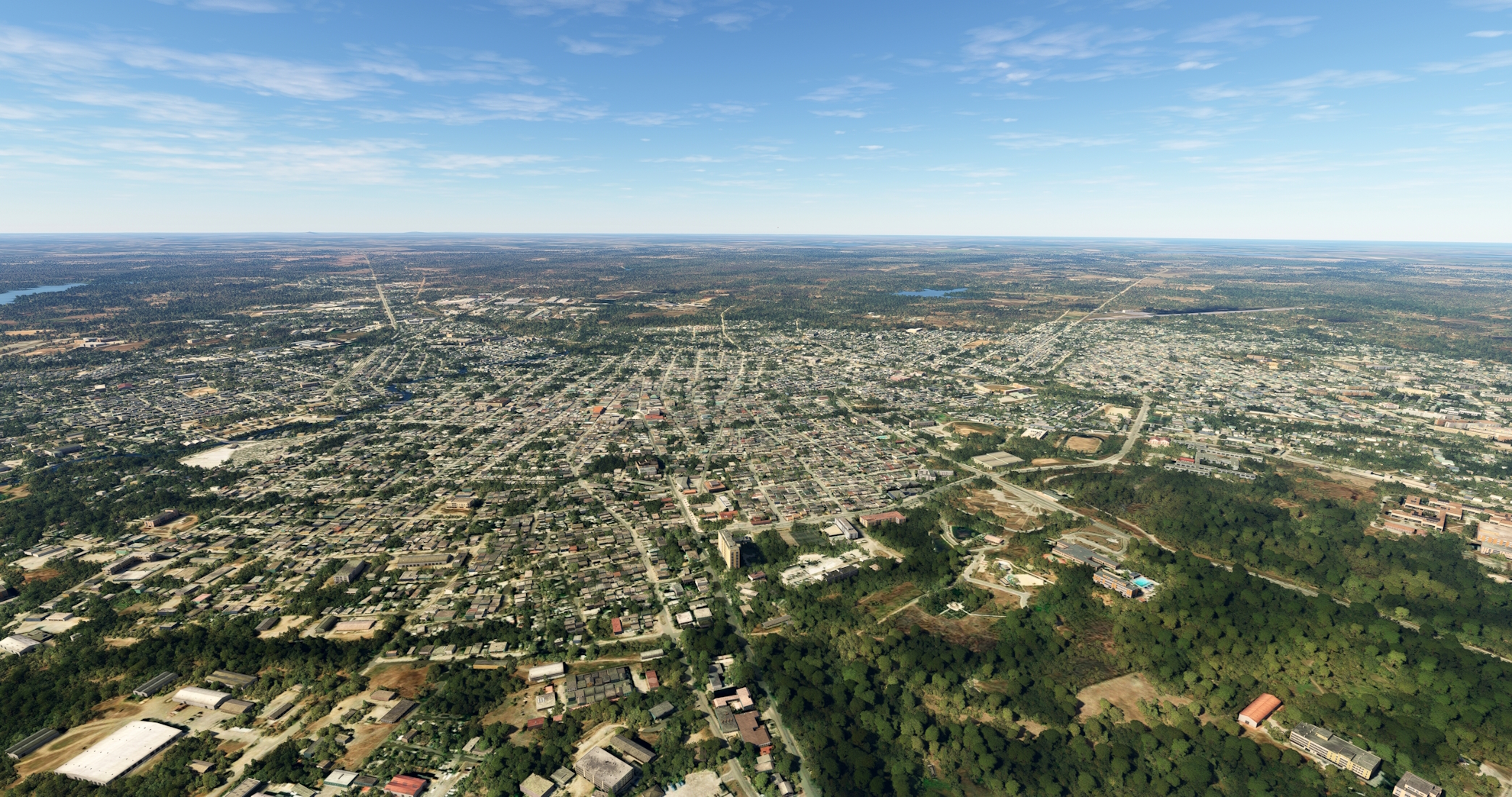
Turn onto a northwestward course and pass over the city of Las Tunas. Las Tunas, founded in 1796, is the capital of the Las Tunas Province of eastern Cuba.
Las Tunas(POI11) to Guáimaro(POI12)
Distance: 22.89NM Bearing: 292° 11 minutes
Turn onto a northwestward course at Las Tunas, paralleling the general course of the Carretera Central, staying to its south. Fly over patchworks of agriculture fields and stands of forest to reach the city of Guáimaro.

Guáimaro(POI12) to Sibanicù(POI13)
Distance: 14.74NM Bearing: 326° 7 minutes
Follow the Carretera Central to the northwest, passing over the small town of Martí where the Cuban Central Railroad intersects the highway. Continue on course from Martí, passing to the south of the town of Cascorro, and then reach the town of Sibanicù.

Sibanicù(POI13) to Siboney(POI14)
Distance: 8.18NM Bearing: 283° 4 minutes
Turn onto a west-northwest heading to the village of Siboney, located directly on the Cuban Central Railroad line and just south of the Central Highway.

Siboney(POI14) to Ap. Internaz. Ignacio Agramonte(MUCM)
Distance: 14.35NM Bearing: 325° 7 minutes
Turn onto a northwest heading at Siboney and pass just south of a large reservoir. Fly over the small hamlet of El Bijabo, and then sight and fly over the prominent peak, Sierra de Maraguán, 614 feet above sea level. Continue on course to Ignacio Agramonte International Airport and land.

Leg 3
Ap. Internaz. Ignacio Agramonte to Ap. Internaz. Di Máximo Gómez
Leg Distance: 70.39 Approximate time at 125kts: 34 minutes.
Ap. Internaz. Ignacio Agramonte(MUCM) to Camagüey(POI15)
Distance: 5.11NM Bearing: 253° 2 minutes
After lifting off from Ignacio Agramonte International Airport, set a course to the southwest and pass over the city of Camagüey. One of the seven original settlements in Cuba founded by the Spanish, Camagüey today is the nation’s third most populous city and is the capital of the Camagüey Province. The United Nations named the old town section of Camagüey a World Heritage Site due to its notable role in Cuba’s colonization and agricultural development.

Camagüey(POI15) to Florida(POI16)
Distance: 18.66NM Bearing: 306° 9 minutes
Turn onto a northwesterly heading and follow the path of the Central Rail line to the city of Florida. Established in the early 1900s, the name is Spanish for “flowery” or “abundant in flowers.”

Florida(POI16) to Gaspar(POI17)
Distance: 21.86NM Bearing: 313° 10 minutes
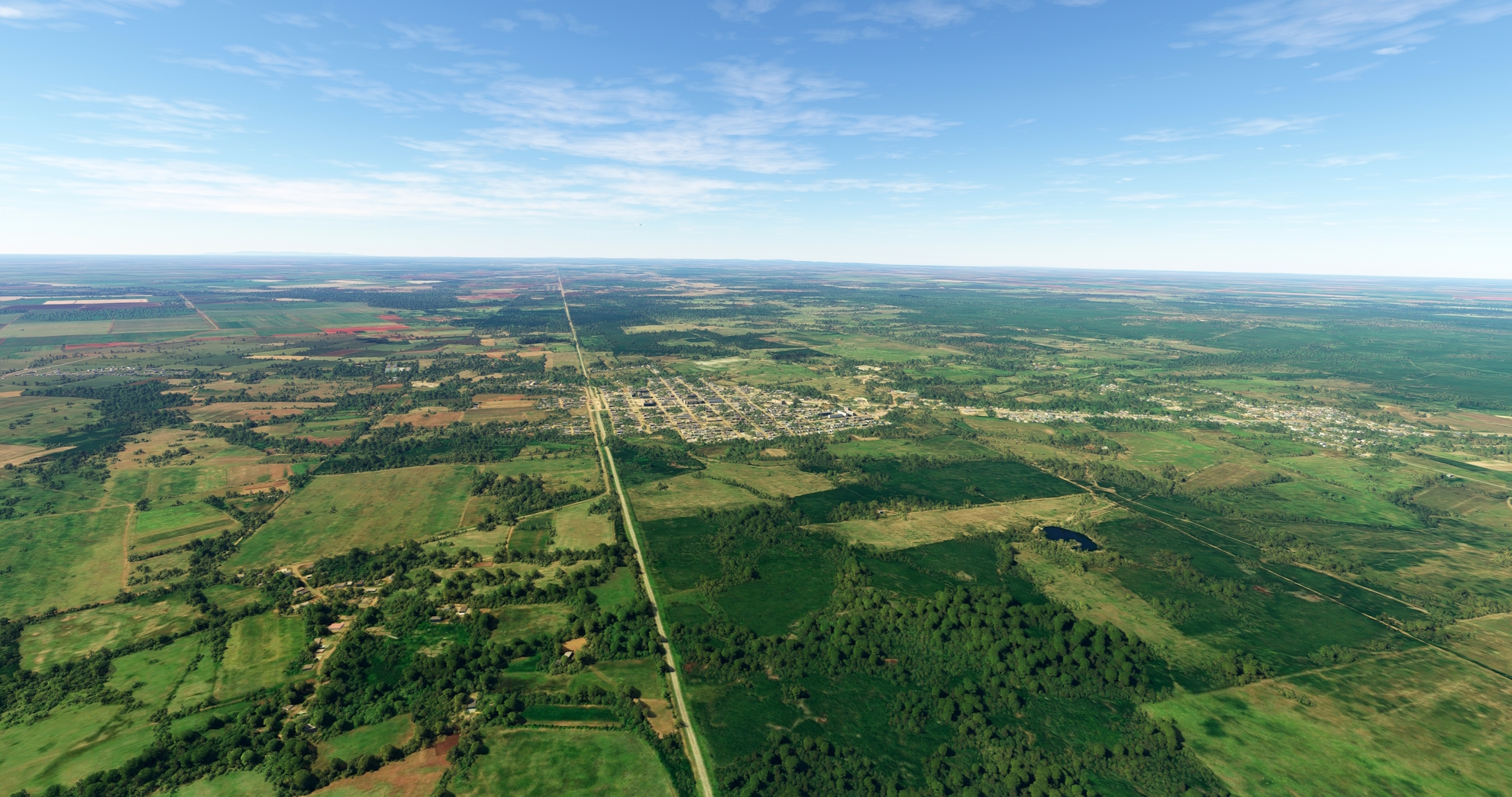
From Florida, continue following the Central Rail line, which parallels the Central Highway. Pass over the town of Carlos Manuel de Céspedes, typically shortened to Céspedes. The town was named after Carlos Manuel de Céspedes, a plantation owner who freed his slaves and drafted the declaration of Cuban Independence, which precipitated the Ten Years’ War. Also known as the Great War, the Ten Years’ War was key in the fight for Cuba’s independence from Spain. Céspedes became the first president of “Cuba in Arms” in 1868. Continue following the rail line after passing over Céspedes, flying over a pastoral mosaic of agriculture fields and forest. Pass over the city of Gaspar, a town founded in 1916 that is known for its goat production.
Gaspar(POI17) to Ciego de Ávila(POI18)
Distance: 13.38NM Bearing: 305° 6 minutes
Continue following the Central Rail line, passing the small villages of Colorado and Vicente, to reach Ciego de Ávila. Ciego de Ávila is the capital of the Ciego de Ávila Province of Central Cuba, and is known for its rich agricultural production, including livestock, potatoes, sugar cane, and pineapples.
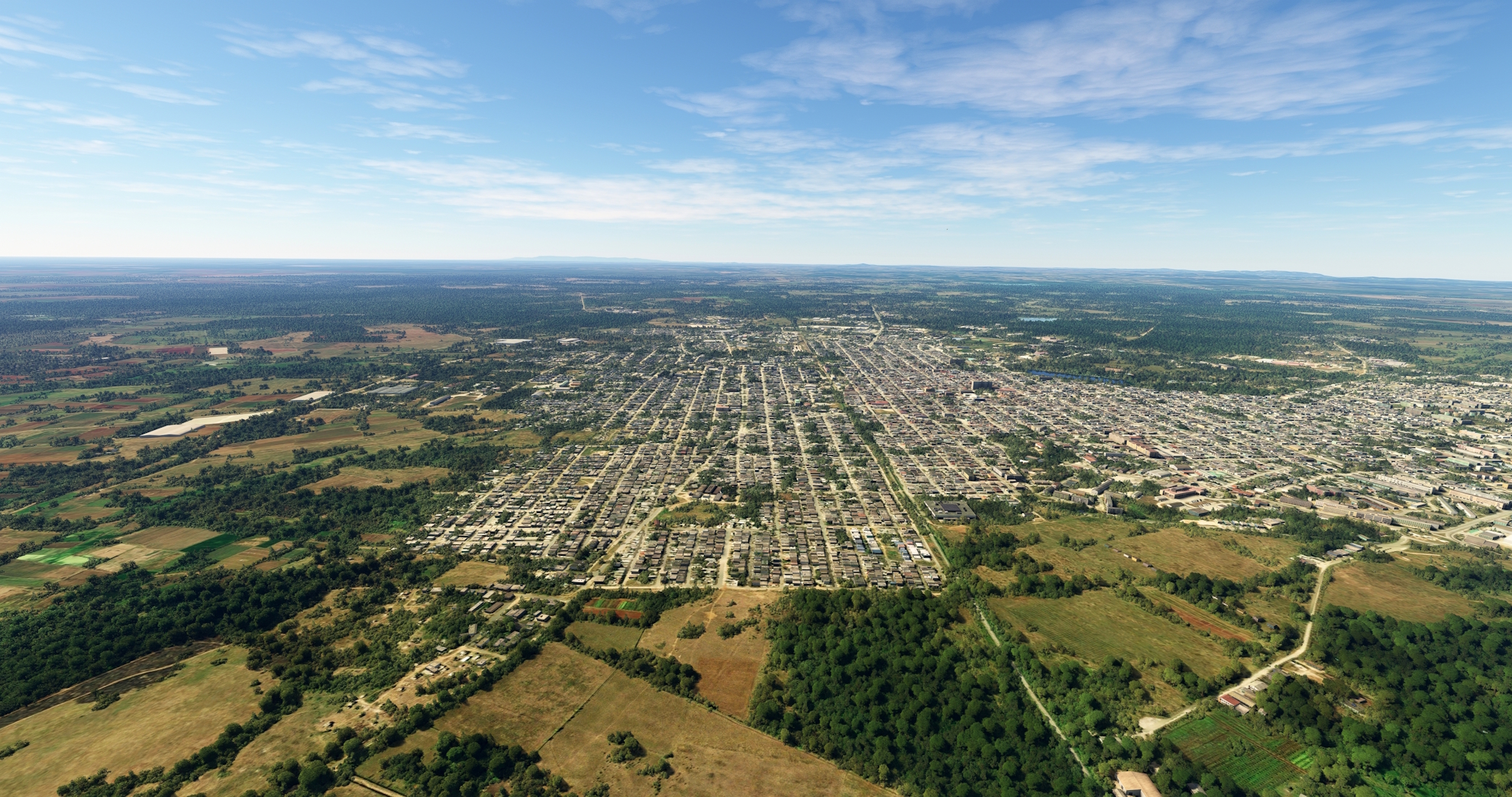

Ciego de Ávila(POI18) to Ap. Internaz. Di Máximo Gómez(MUCA)
Distance: 11.38NM Bearing: 359° 5 minutes
Once over Ciego de Ávila, turn to the northwest and parallel a spur rail line away from the Central Rail line. Skirt the eastern side of the Black Forest (Bosque Negro), which lies northwest of Ciego de Ávila. Maintain heading, passing to the west of the village of Ceballos. Gain a visual on and land at the single-runway Máximo Gómez Airport.

Leg 4
Ap. Internaz. Di Máximo Gómez to Abel Santamaría
Leg Distance: 71.23 Approximate time at 125kts: 34 minutes.
Ap. Internaz. Di Máximo Gómez(MUCA) to Tamarindo(POI19)
Distance: 8.42NM Bearing: 317° 4 minutes
After taking to the Cuban skies from Máximo Gómez Airport, set a course to the northwest and gain a visual on two large reservoirs that are situated side-by-side: Liberación de Florencia reservoir on the west and Cañada Blanca reservoir on the east. Fly over rolling, forested terrain to reach the village of Tamarindo, which lies just to the southeast of the Cañada Blanca reservoir.
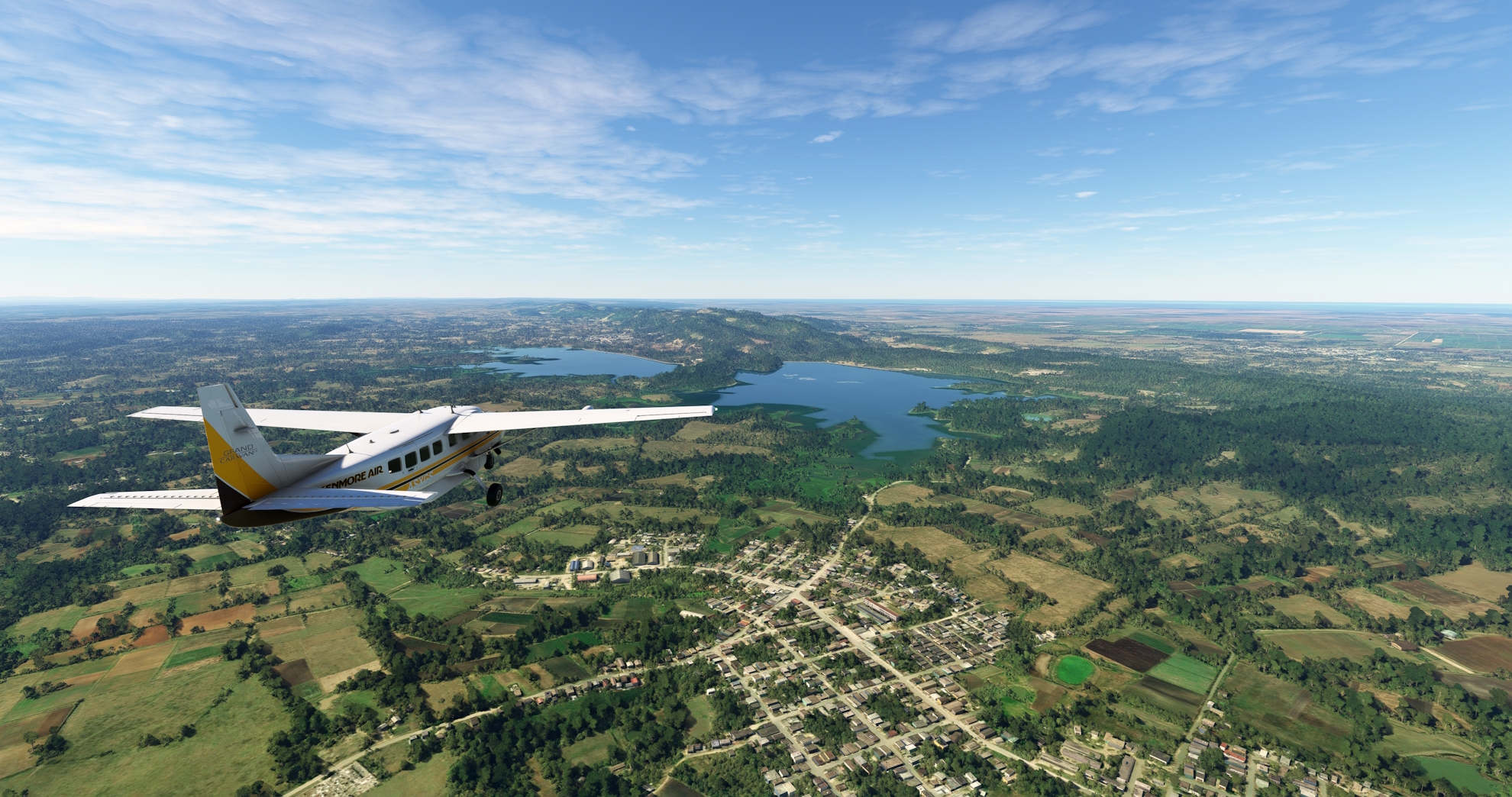

Tamarindo(POI19) to Florencia(POI20)
Distance: 4.14NM Bearing: 304° 2 minutes
Continue on course to the northwest from Tamarindo and fly over the eastern portion of Liberación de Florencia reservoir. The city of Florencia is located on the northwestern side of the reservoir, at the southern base of the Jatibonico Mountains. The small range is known for its lush forests, subterranean cave complexes, and rivers. The area surrounding Florencia is a renowned Tobacco growing region.

Florencia(POI20) to Iguara(POI21)
Distance: 15.81NM Bearing: 291° 8 minutes
From Florencia, follow the Northern Line railroad and the Jarahueca-Florencia highway to the north-northwest. The route follows the southern base of the Jatibonico Mountains and offers spectacular views of this part of Cuba, which is renowned as one of the nation’s most picturesque. Pass over the small villages of Perea and Venegas and then reach the town of Iguara.
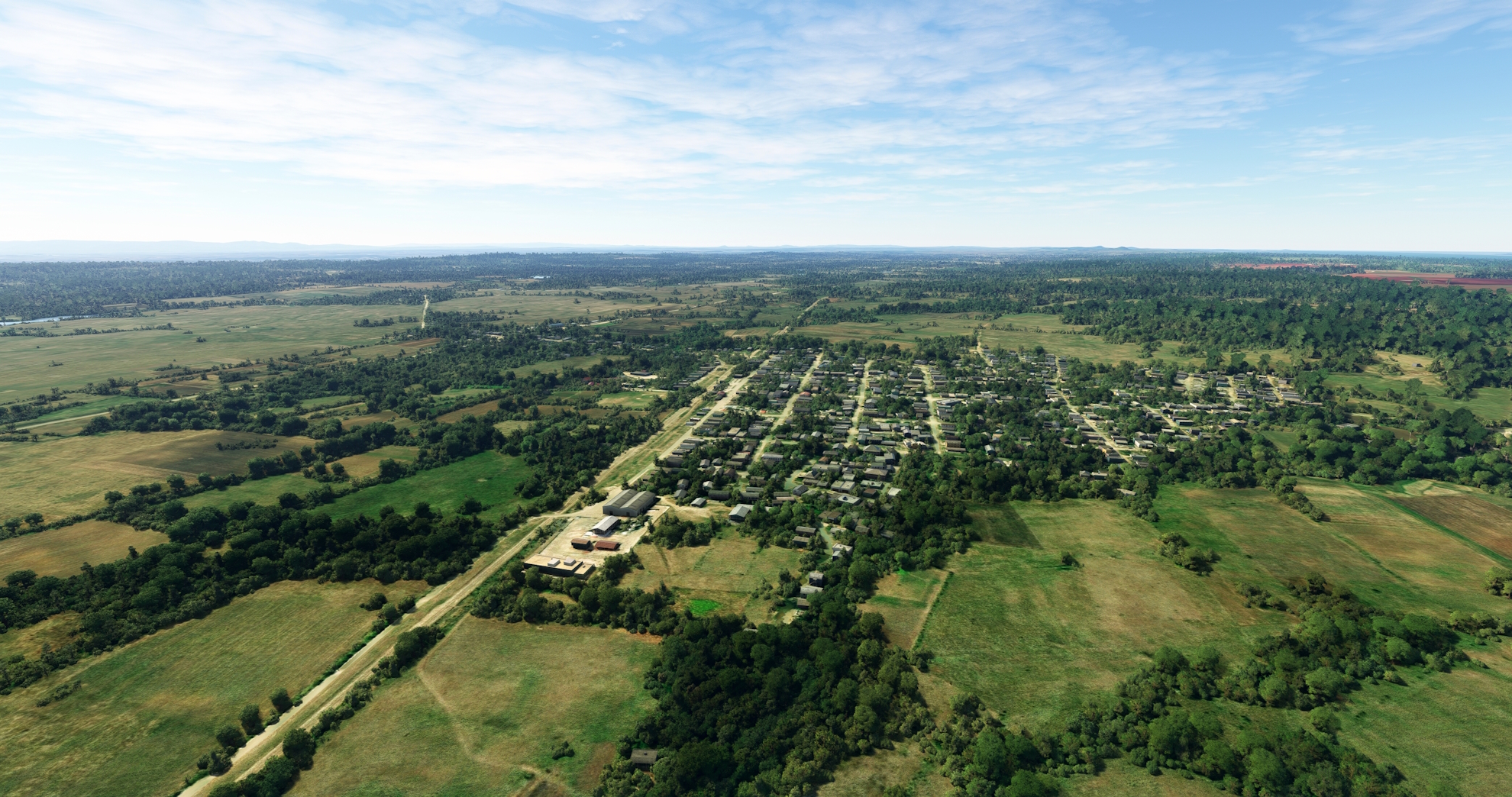

Iguara(POI21) to General Carrillo(POI22)
Distance: 8.99NM Bearing: 300° 4 minutes
Continue following the Northern Line to the town of General Carrillo. The town was named for Francisco Carrillo Morales, a commanding general during the Cuban War of Independence and the sixth Vice President of Cuba.

General Carrillo(POI22) to Placetas(POI23)
Distance: 14.67NM Bearing: 289° 7 minutes
Parallel the Northern Line rail line to the small town of Remate de Ariosa, where the line turns more to the north. Continue on course to the north-northwest, flying over the boundary of agriculture fields to the north and forest to the south, and reach the town of Placetas. The central Cuban town was founded as a center of sugar cane production, and today is known for its tobacco.

Placetas(POI23) to Minerva Reservoir(POI24)
Distance: 9.7NM Bearing: 316° 5 minutes
At Placetas, turn onto a course to the northwest and pass over the Minerva Reservoir (Embalse Minerva), known for its freshwater aquaculture, notably its tilapia production.

Minerva Reservoir(POI24) to Abel Santamaría(MUSC)
Distance: 9.5NM Bearing: 306° 5 minutes
Continue on course over the Minerva Reservoir, then sight the Ochoa River where it intersects with a rail line and pass over the intersection. Fly over the town of La Guayaba and then land at the Abel Santamaría Airport, an international facility that serves the city of Santa Clara to its south.

Leg 5
Abel Santamaría to Jaime González
Leg Distance: 77.58 Approximate time at 125kts: 37 minutes.
Abel Santamaría(MUSC) to Santa Clara(POI25)
Distance: 5.41NM Bearing: 203° 3 minutes
Lift off from Abel Santamaría Airport and set a course to the south and fly over the city of Santa Clara. Located near the geographic center of Cuba, Santa Clara is the capital of Villa Clara and the nation’s fifth most populous city. It is a historically important city, as it was the location of the Battle of Santa Clara, which was the final battle of the Cuban Revolution, after which Fidel Castro’s forces seized control of Cuba. Today it is an important university town and has a number of historic attractions related to the Cuban Revolution.

Santa Clara(POI25) to Mataguá(POI26)
Distance: 10.19NM Bearing: 195° 5 minutes
Continue to the south after passing over Santa Clara, following the Santa Clara-Manicaragua Highway to the town of Mataguá.

Mataguá(POI26) to Manicaragua(POI27)
Distance: 5.61NM Bearing: 178° 3 minutes
Following the Santa Clara-Manicaragua Highway to the south, pass over the low Sierra de Potrerillo, a line of hills that is part of the greater Escambray Mountains. Continue south to reach Manicaragua, a city nestled in the Escambray Mountains that is known for its tobacco and coffee production. Manicaragua is renowned as one of the most beautiful locations in Cuba.
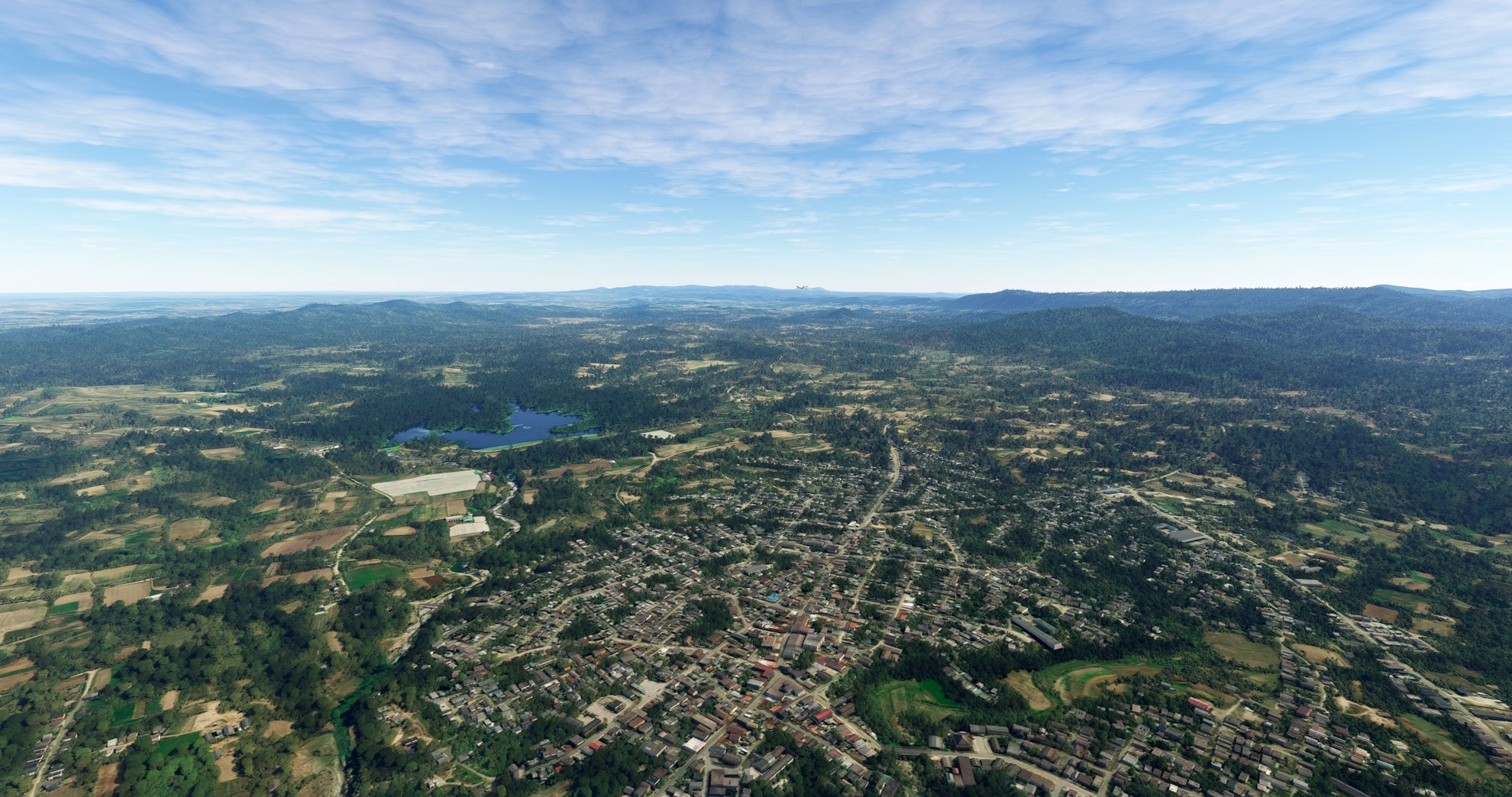

Manicaragua(POI27) to Hanabanilla Lake(POI28)
Distance: 7.34NM Bearing: 202° 4 minutes
Over the city of Manicaragua, gain a visual on the Manicaragua-Topes Highway, which strikes south into the Escambray Mountains. Parallel the general trend of the highway, remaining to its west, and gain a visual on Hanabanilla Lake (Lago Hanabanilla), a large reservoir. Increase altitude due to the increasing height of the peaks to the south, and fly over the eastern end of the reservoir near its dam. Hanabanilla Lake is a popular tourist destination in Cuba due to its beautiful mountain surroundings.
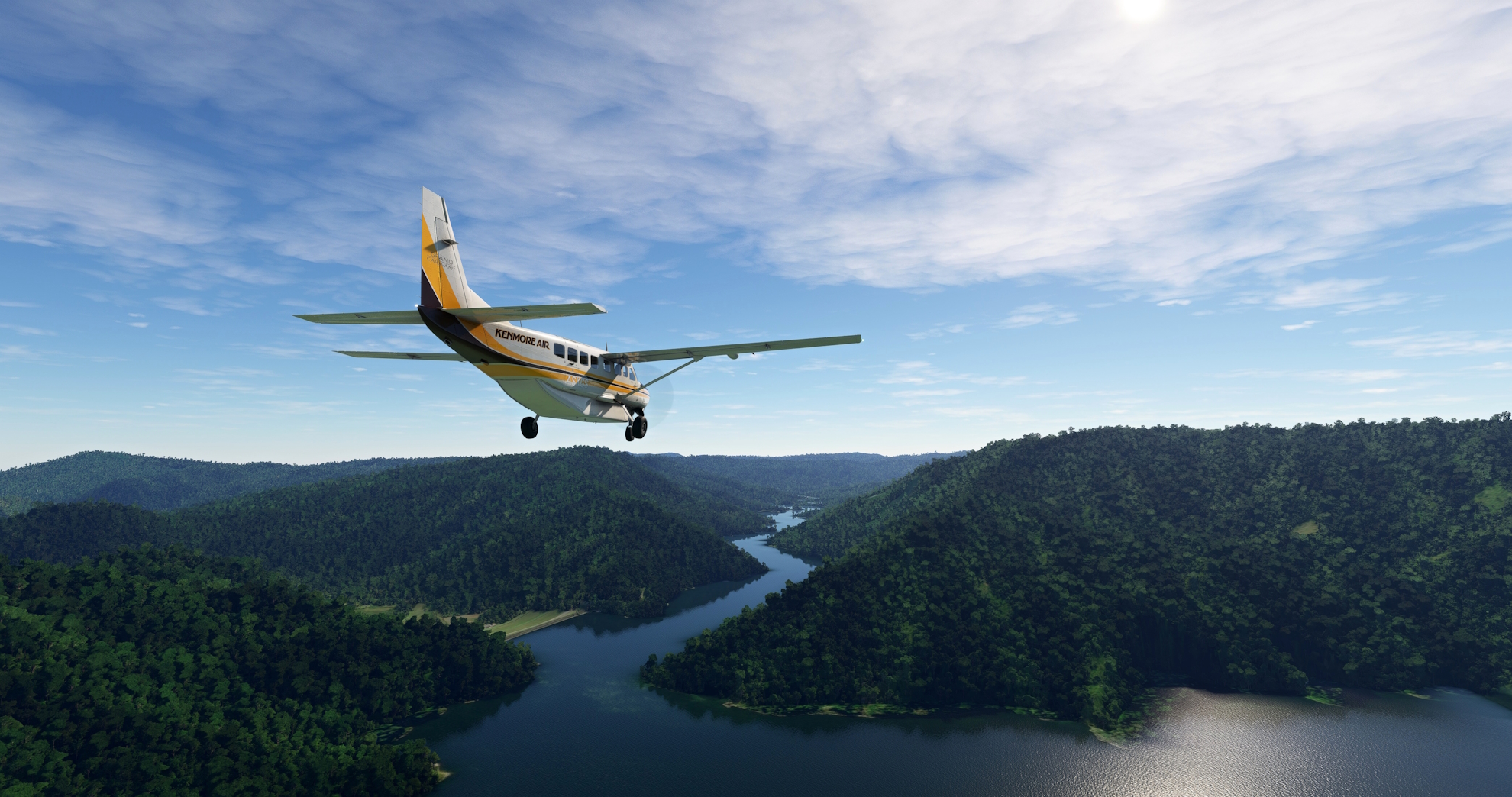

Hanabanilla Lake(POI28) to Trinidad(POI29)
Distance: 13.59NM Bearing: 181° 7 minutes
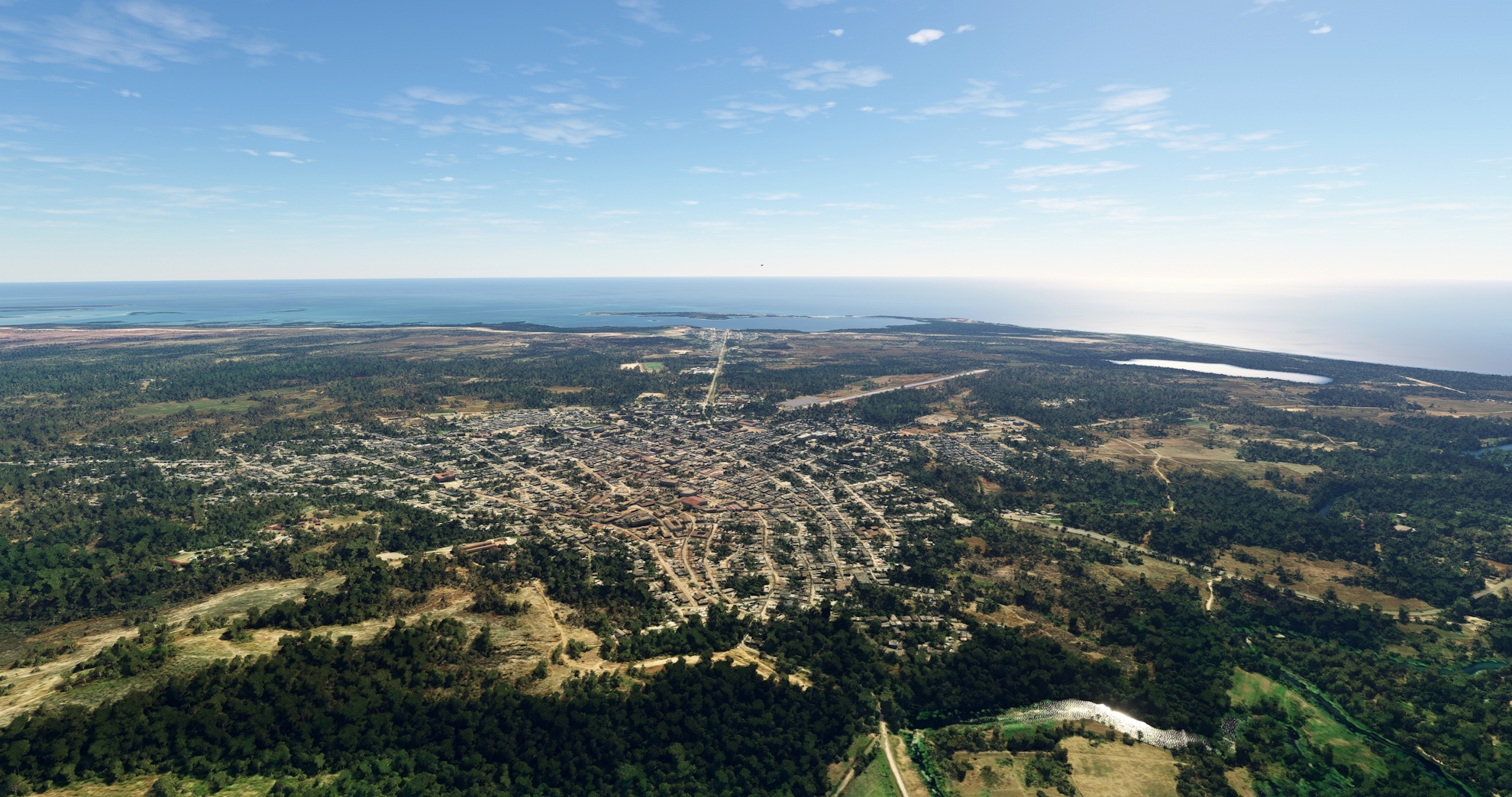
Over Hanabanilla Lake, turn onto a course just east of due south and climb to an altitude of at least 3,000 feet above sea level. Gain a visual on the Caribbean Sea in the distance and the southern coast of Cuba. After passing over the crest of the Escambray Mountains, descend in altitude toward the sea. Sight the hook-shaped Ancon Beach (Playa Ancon), a long sandspit that forms Casilda Bay (Bahía de Casilda). The city of Trinidad, renowned for its sugar cane production, is located on the shores of Casilda Bay. Maintaining a course to Trinidad, pass by the western margin of Valle de los Ingenios, the Valley of the Sugar Mills. A complex of three valleys, Valle de los Ingenios was once home to more than fifty sugar cane mills. The United Nations designated Trinidad and Valle de los Ingenios a World Heritage Site as it is one of the best-preserved sugar cane centers throughout the Caribbean.
Trinidad(POI29) to Camilo Cienfuegos(POI30)
Distance: 14.69NM Bearing: 296° 7 minutes
After passing over Trinidad, turn onto a northwestward course and follow the dramatic, mountainous coastline. Pass over a number of rivers and reach the town of Camilo Cienfuegos, named after Camilo Cienfuegos Gorriarán, one of the key figures in the Cuban Revolution of 1953-1959.

Camilo Cienfuegos(POI30) to Playa Rancho de Luna(POI31)
Distance: 13.98NM Bearing: 319° 7 minutes
Continue on a northwest course, following the coastline. Gain a visual on Cienfuegos Bay (Bahía de Cienfuegos) and fly to Playa Rancho de Luna (Ranch of the Moon Beach), located just to the east of the opening of Cienfuegos Bay to the Caribbean Sea.

Playa Rancho de Luna(POI31) to Jaime González(MUCF)
Distance: 6.77NM Bearing: 10° 3 minutes
At Playa Rancho de Luna, turn to the northwest and skirt the eastern edge of Cienfuegos Bay (Bahía de Cienfuegos), one of Cuba’s most important natural harbors and home to two ports. Land at the single-runway Jaime González Airport, which serves the city of Cienfuegos. Cienfuegos, the capital of the Cienfuegos Province, is an important industrial center in Cuba.

Leg 6
Jaime González to Aeroporto Di Colón
Leg Distance: 49.12 Approximate time at 125kts: 24 minutes.
Jaime González(MUCF) to Damuji Reservoir(POI32)
Distance: 11.05NM Bearing: 328° 5 minutes
Lift off from Jaime González Airport and set a course to the northwest. Pass over the small village of Venta del Río and sight the Damuji Reservoir (Embalse Damuji), located north of the northwestern end of Cienfuegos Bay.
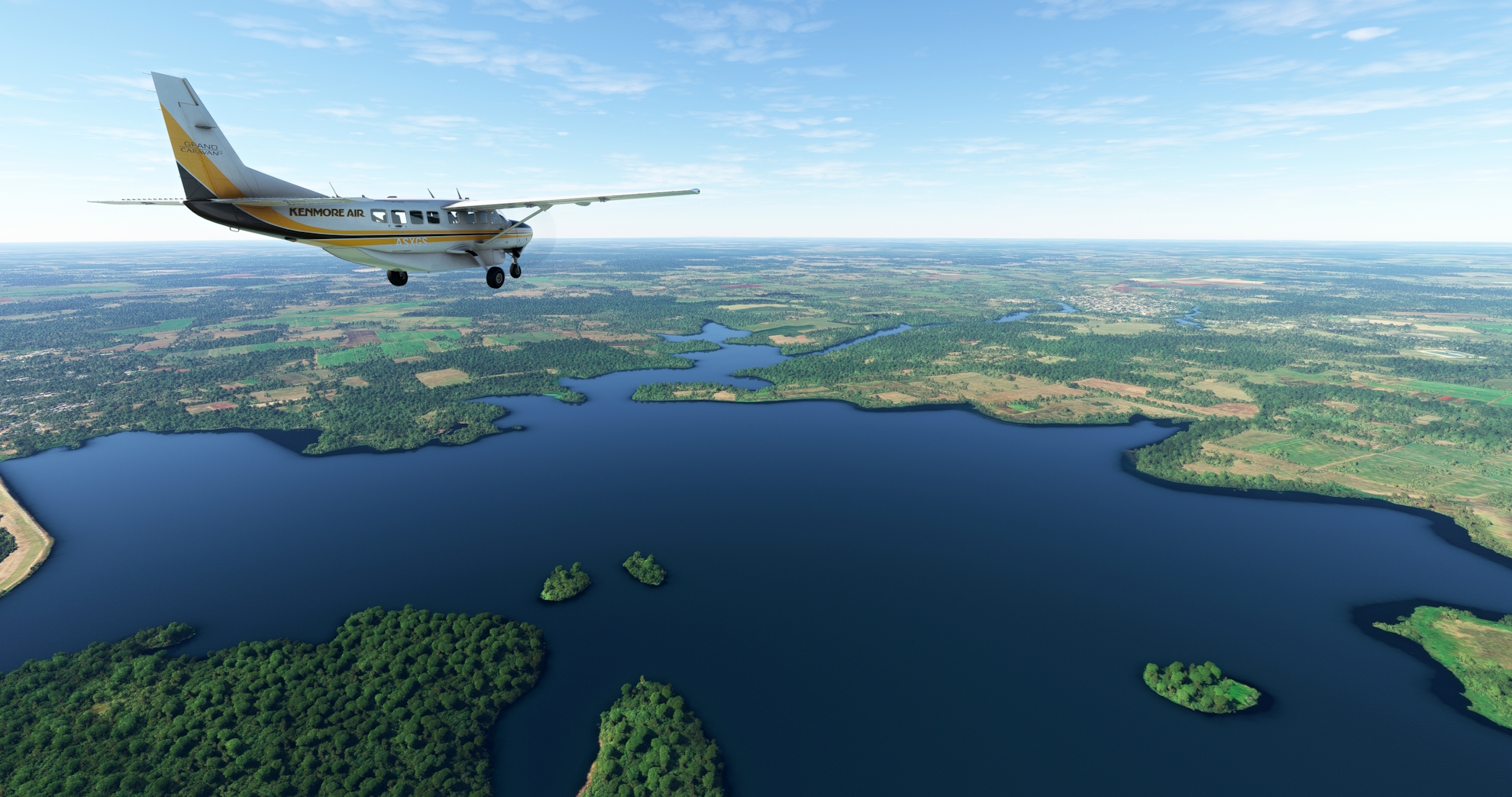

Damuji Reservoir(POI32) to Aguada de Pasajeros(POI33)
Distance: 17.55NM Bearing: 294° 8 minutes
Adjust course onto a west-northwest heading over Damuji Reservoir. Fly over agriculture fields and a line of forest, then sight the town of Aguada de Pasajeros, located along the A1 Motorway.
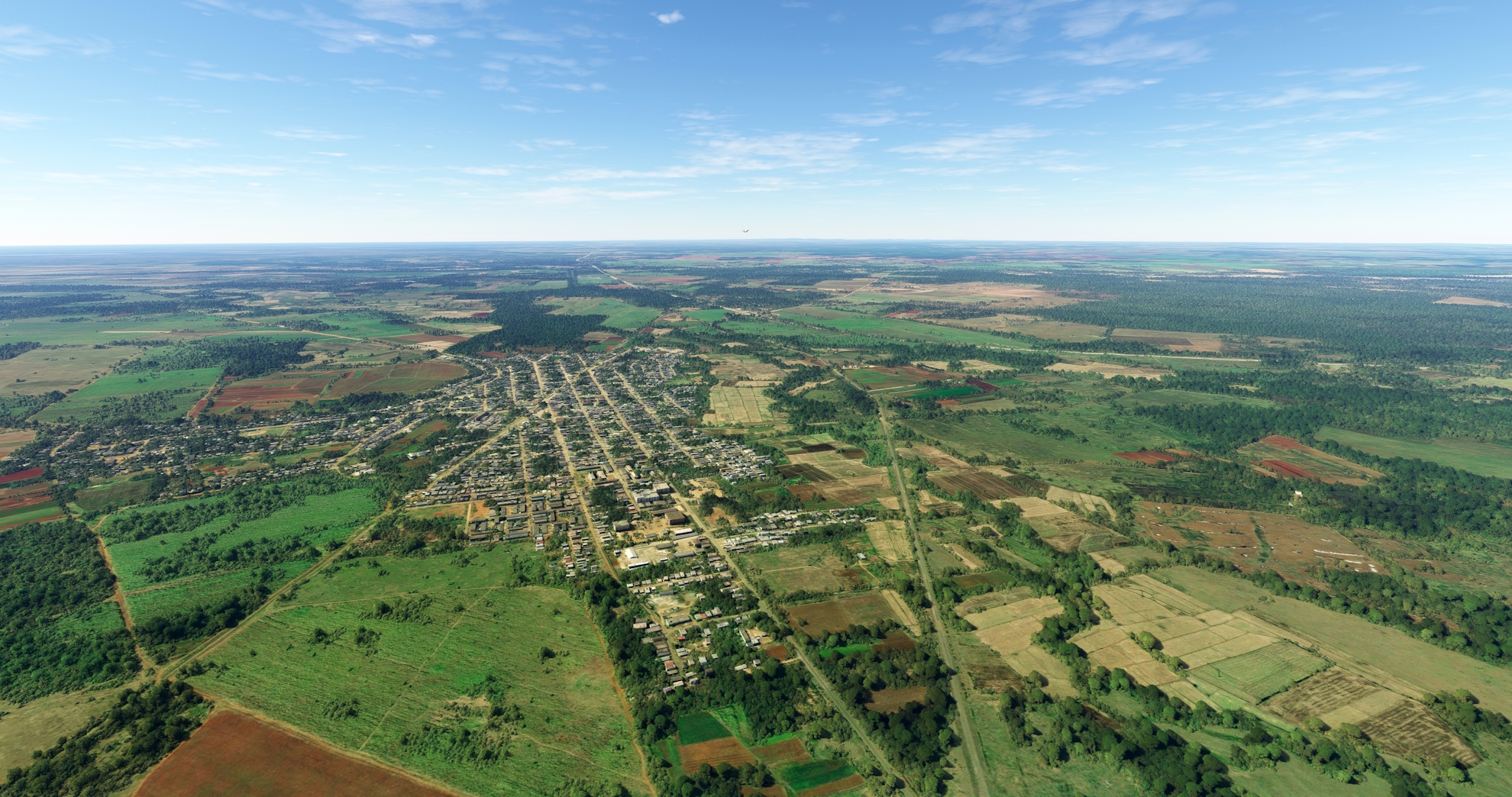
Aguada de Pasajeros(POI33) to Calimete(POI34)
Distance: 9.93NM Bearing: 345° 5 minutes
Turn onto a northwest heading at Aguada de Pasajeros and parallel the general course of the Circuito Sur (Southern Circuit) highway. Pass to the east of the small town of Amarillas and then fly over Calimete. Calimete was the location of the Battle of Calimete, which took place on December 29, 1859 during the Cuban War of Independence.

Calimete(POI34) to Aeroporto Di Colón(MUCO)
Distance: 10.59NM Bearing: 1° 5 minutes
Follow the Circuito Sur to the town of Colón and land at Colón Airport, located on the south side of the town.

Leg 7
Aeroporto Di Colón to Ap. Internaz. José Martí
Leg Distance: 93.88 Approximate time at 125kts: 45 minutes.
Aeroporto Di Colón(MUCO) to Jovellanos(POI35)
Distance: 16.12NM Bearing: 297° 8 minutes
After lifting into the Cuban sky at Colón Airport, turn onto a course to the west-northwest and parallel the course of the Carretera Central de Cuba (Central Highway of Cuba) to the agricultural town of Jovellanos.

Jovellanos(POI35) to Limonar(POI36)
Distance: 14.72NM Bearing: 312° 7 minutes
Continue following the Carretera Central to the northwest, passing along the eastern periphery of a small line of forested hills. Continue to the small town of Limonar. Limonar is located in the heart of the Matanzas Province, which stretches from the north to the south of Cuba. Matanzas is one of Cuba’s most economically important provinces due to agriculture and petroleum production.

Limonar(POI36) to Matanzas(POI37)
Distance: 10.61NM Bearing: 306° 5 minutes
Maintain heading and gain a visual on Matanzas Bay (Bahía de Matanzas). The bay is part of the Florida Strait, where the waters of the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean meet. The bay is 100 miles due south of Key West, Florida, one of Cuba’s closest points to Florida. The city of Matanzas, the capital of the Cuban province of Matanzas, is located just inland of the western end of the bay. The city boasts a rich culture, with a history of poets, musicians, and dancers. Located just over 50 miles to the east of Cuba’s Capital, Havana, Matanzas is a popular tourist destination and is home to a variety of museums, theaters, and cathedrals.

Matanzas(POI37) to Aguacate(POI38)
Distance: 13.88NM Bearing: 264° 7 minutes
Turn onto a south-southwesterly course over Matanzas and follow the general trend of the Central Highway, remaining to its north. Pass just to the south of Caunavaco Reservoir (Embalse Caunavaco). Continue on course to the town of Aguacate.

Aguacate(POI38) to San José de las Lajas(POI39)
Distance: 17.89NM Bearing: 271° 9 minutes
Continue on a westward track and sight Mampostón Reservoir (Embalse Mampostón) in the distance. Fly over the center point of the reservoir and pass over the city of San José de las Lajas. San José de las Lajas is the capital of Mayabeque Province, which was formed on January 1, 2011 after the Cuban government separated it and another province, Artemisa Province, from the former La Habana Province. San José de las Lajas is an important educational, commercial, and industrial center for Cuba.

San José de las Lajas(POI39) to Havana(POI40)
Distance: 14.07NM Bearing: 309° 7 minutes
At San José de las Lajas, turn onto a northwest heading and follow the Central Highway into Havana. Havana is Cuba’s capital and most populous city with a population of over 2.3 million people. The city was founded in the 16th century on the bay that is today Havana Harbor, the country’s busiest port. Havana was a tremendously important port for the Spanish due to its location and it became one of the New World’s most important centers of trade. Since its founding, Havana has grown into a national center of industry and education. The city is renowned for its varied architecture, including El Morro Castle, which stands at the entrance to Havana Bay and the Havana Cathedral.
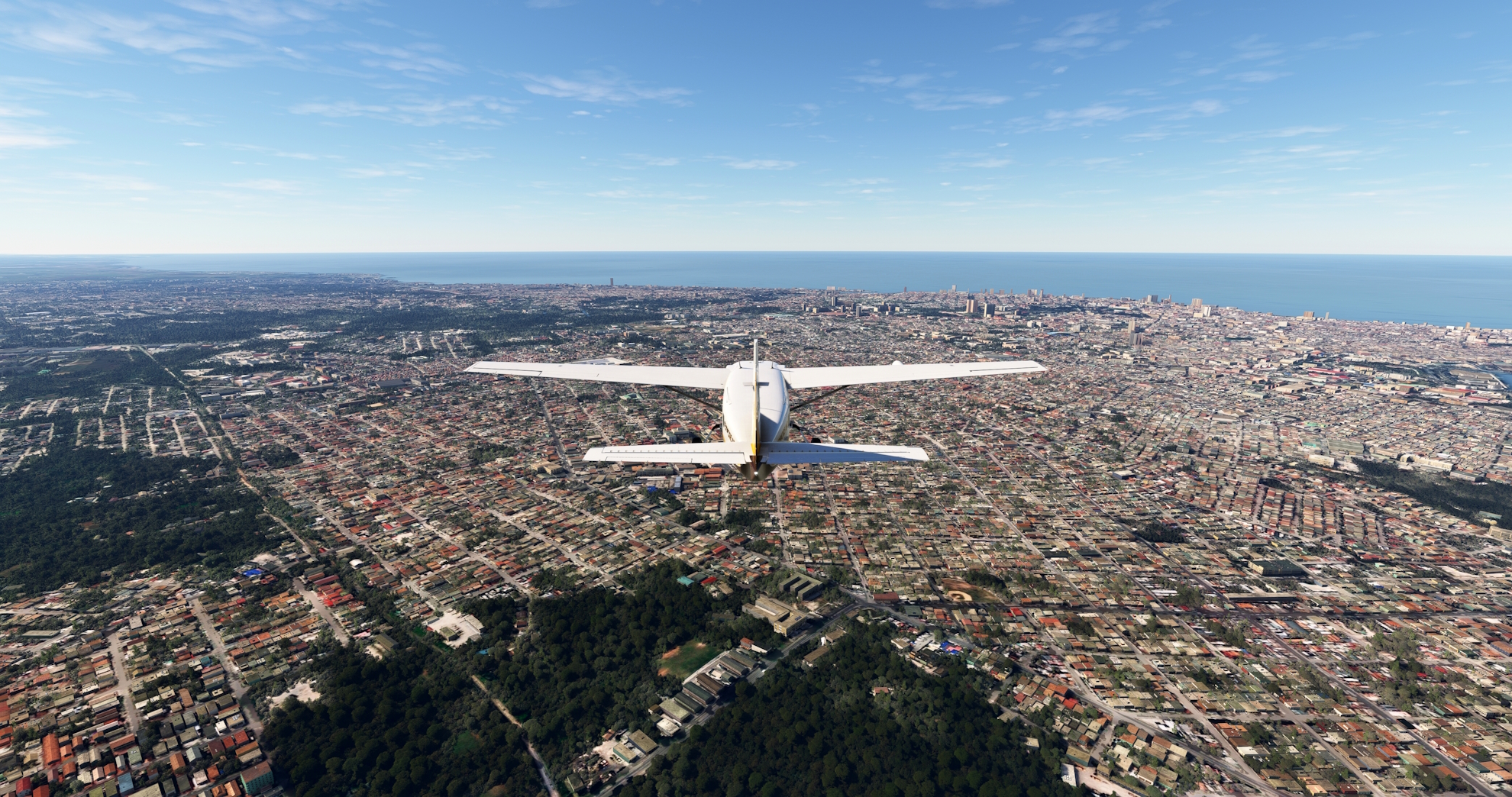

Havana(POI40) to Ap. Internaz. José Martí(MUHA)
Distance: 6.59NM Bearing: 210° 3 minutes
Over Havana, turn onto a southwest heading and land at José Martí International Airport, bringing this journey through Cuba to an end.

