Haiti and the Dominican Republic are countries filled with mesmerizing history, culture, and natural beauty. The Dominican Republic is located on the eastern portion Hispaniola, an island that lies where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the North Atlantic Ocean. Cuba lies to the island’s west and Puerto Rico to its east. Hispaniola is the second largest of the Greater Antilles archipelago (after Cuba) and the second largest of the West Indies, of which the Greater Antilles is a part. Haiti, the Dominican Republic’s neighbor, occupies the western portion of Hispaniola.
The Dominican Republic is the second largest nation in the Caribbean. It measures just over 240 miles from its easternmost point, Cape Engaño, to its westernmost point, its border with Haiti near the village of Las Lajas. The country is 176 miles wide, as measured from its northernmost point, Cabo Isabela, to its southernmost point, Alto Velo Island. Haiti is the third largest country in the Caribbean and it spans 180 miles east-to-west and 130 miles north-to-south. Haiti is a little more than half the size of the Dominican Republic in area.
Hispaniola boasts an incredibly diverse range of landscapes for an island of its size. It has world-renowned white-sand beaches, four distinct mountain ranges, lush stands of forests, and even some arid regions. It boasts the highest point in the Caribbean, Pico Duarte, and the lowest point in the Caribbean, Lake Enriquillo.
Haiti and the Dominican Republic experience a wide range of climates due to their varied terrain. They have a tropical climate at their lower elevations, with consistently warm temperatures year-round. Microclimates exist throughout interior mountains and valleys; these include rainforest, hot semi-arid, tropical savanna, and in some locations, subtropical highland climates.
The Taíno, indigenous Caribbean people, are the earliest known human inhabitants of the island of Hispaniola and what would become the Dominican Republic and Haiti. Christopher Columbus, the first European to visit Hispaniola, arrived on Christmas Eve, 1492. He named the island “Española” (Little Spain), a name which eventually evolved into “Hispaniola.” Columbus established the first permanent European presence in the New World, a fort called La Navidad, at a location at what is today northeast Haiti, close to the border with the Dominican Republic.
The ensuing centuries following the arrival of Columbus witnessed tremendous changes and turmoil. The Spanish and French established colonies to exploit the island’s natural riches and its strategic position in the New World. Indigenous people were enslaved, slaves from Central and West Africa were brought to Hispaniola, and independence movements erupted. The island was eventually divided into two countries, Haiti on the west, and the Dominican Republic on the east.
Haiti and the Dominican Republic are two of the most wonderfully diverse nations on the planet, both in terms of cultural heritage and natural splendor. This bush trip celebrates the very best of the Dominican Republic and Haiti through a circumnavigation route of Hispaniola, visiting coasts, mountains, valleys, cities, and towns of both countries.
Total Legs: 6 Total Distance: 490 Total Time(125kts): 3 hours 55 minutes
Leg 1
Maria Montez Intl to Toussaint Louverture Airport
Leg Distance: 70.42 Approximate time at 125kts: 34 minutes.
Maria Montez Intl(MDBH) to Rincón Lagoon(POI1)
Distance: 6.7NM Bearing: 295° 3 minutes
After lifting off from María Montez International Airport, set a course to the west-northwest and parallel highway RD-46, staying to its north. Gain a visual on Rincón Lagoon (Laguna Rincón), a large lagoon. Pass to the north of the town of Cabral and fly over the lagoon. Rincón Lagoon, also called Cabral Lagoon (Laguna de Cabral), is the largest freshwater lagoon in the Dominican Republic and was designated as a reserve due to its rich plant and animal life. Species that live in the lagoon include herons, ducks, iguanas, freshwater turtles, flamingos, and pelicans.

Rincón Lagoon(POI1) to La Colonia(POI2)
Distance: 13.51NM Bearing: 305° 6 minutes
Continue on course from Rincón Lagoon, passing over the village of Cristóbal, located on the lagoon’s western shore. Parallel highway RD-46 toward the small village of La Colonia. Pass over La Gran Sabana National Park, which protects vast stretches of cactus forest, dry forest, and salt wetlands. Pass over the village of La Colonia, which lies directly on highway RD-46.

La Colonia(POI2) to Lake Enriquillo(POI3)
Distance: 9.83NM Bearing: 298° 5 minutes
From La Colonia, continue on course, paralleling highway RD-46, staying just to its north. Pass just north of Duvergé, the most populous city in the country’s province of Independencia, and gain a visual on Lake Enriquillo (Lago Enriquillo). Continue on course and pass over the southeastern corner of the lake. Lake Enriquillo is the largest lake in both the Dominican Republic and the Island of Hispaniola. At 151 feet below sea level, it is the lowest point in the Dominican Republic, the lowest on the island of Hispaniola, the lowest point in the Caribbean, and the lowest point of any island country on the planet. It is home to a variety of animal species, including the American flamingo, two endangered iguana species, and the Caribbean’s largest population of American crocodile.

Lake Enriquillo(POI3) to El Limón(POI4)
Distance: 9.31NM Bearing: 287° 4 minutes
Continue on course, following highway RD-46, to El Limón, a small village that developed based on local agriculture, notably the cultivation of bananas.

El Limón(POI4) to Lake Azuéi(POI5)
Distance: 6.33NM Bearing: 316° 3 minutes
Follow highway RD-46 to the northwest from El Limón. Pass over the city of Jimaní, the capital of the Dominican Republic’s Independencia Province, to reach the eastern shore of Lake Azuéi. Also known as Étang Saumâtre (“brackish pond” in French), most of the lake lies in Haiti. The international border is located within a mile of the easternmost shore of the lake.

Lake Azuéi(POI5) to Nan Codastre(POI6)
Distance: 17.69NM Bearing: 295° 8 minutes
Follow the southern shoreline of the lake and pass into Haiti. Traverse the southernmost extremity of the lake and pass back over land at Village Miracle. Follow National Route 8 (RN 8) to the village of Nan Codastre. Although Haiti and the Dominican Republic share the same island and some history, the two nations are distinct culturally and economically. While Spanish is the language of the Dominican Republic, Haitians speak French and Haitian Creole. Economically, the Dominican Republic has developed at a faster pace than Haiti in the past half century.

Nan Codastre(POI6) to Port-au-Prince(POI7)
Distance: 4.58NM Bearing: 295° 2 minutes
Continue following RN 8 to Port-au-Prince, the capital and most populous city in Haiti with more than 2.5 million inhabitants in its greater metropolitan area. Port-au-Prince is located at the head of Port-au-Prince Bay, which opens to the Gulf of Gonâve, part of the Caribbean Sea. Haiti is the third largest nation in the Caribbean by area, after Cuba and the Dominican Republic. The country traces its modern lineage to Spanish and then French colonists, who established a lucrative industry of sugarcane production in the area. Today, agriculture plays a vital role in Haiti’s economy, and it exports a variety of crops, including coffee, papayas, mangoes, and vetiver, a root plant used for perfumes. Port-au-Prince is the country’s most important shipping port.

Port-au-Prince(POI7) to Toussaint Louverture Airport(MTPP)
Distance: 2.47NM Bearing: 276° 1 minutes
Pass over the Gray River (Rivière Grise) and then land at Toussaint Louverture International Airport, located just inland of Port-au-Prince Bay.

Leg 2
Toussaint Louverture Airport to Cap Haitien Intl
Leg Distance: 79.82 Approximate time at 125kts: 38 minutes.
Toussaint Louverture Airport(MTPP) to Mirebalais(POI8)
Distance: 18.58NM Bearing: 46° 9 minutes
Lift off from Toussaint Louverture International Airport and set a course to the northeast, paralleling National Route 3 (RN 3), remaining to its west. Pass over a small range of hills and then pass over the city of Mirebalais, located at the confluence of a number of rivers.
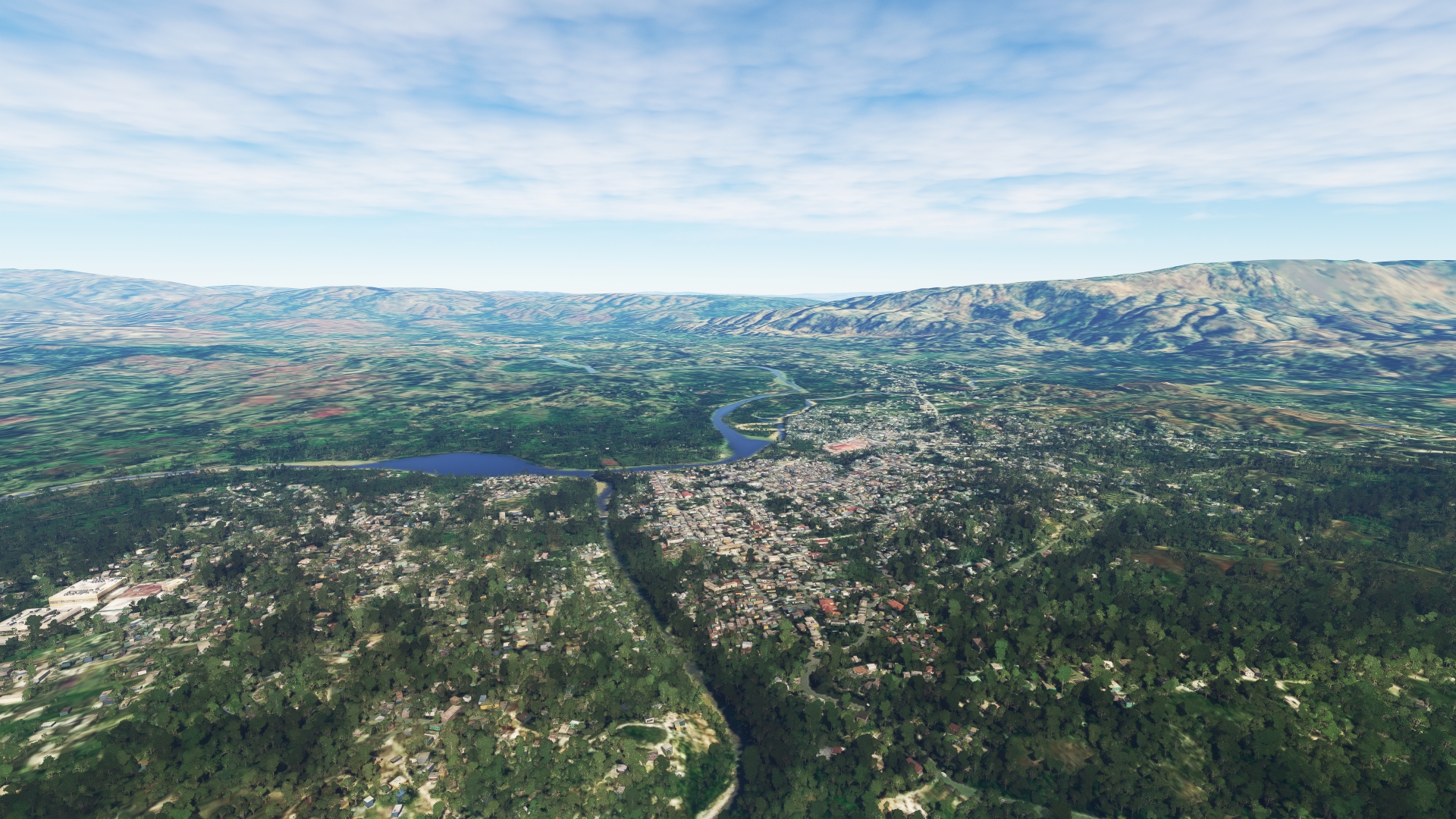

Mirebalais(POI8) to Lake Péligre(POI9)
Distance: 5.69NM Bearing: 54° 3 minutes
Continue on course to the northeast and gain a visual on Lake Péligre, the second largest lake in Haiti. The lake is a reservoir that formed on the Artibonite River with the construction of the Péligre Dam, the tallest dam in Haiti. Pass over the western extremity of the lake and the Péligre Dam.

Lake Péligre(POI9) to Thomonde(POI10)
Distance: 8.07NM Bearing: 41° 4 minutes
Continue to the northeast, following the general trend of National Route 3 through the mountains. Gain a visual on the Thomonde River, which flows through heavily forested hills. Pass over the town of Thomonde, located just north of the river.

Thomonde(POI10) to Hinche(POI11)
Distance: 7.88NM Bearing: 353° 4 minutes
Follow National Route 3 to the northwest into a broad, forested valley. The city of Hinche lies at the bottom of the valley at the confluence of a number of rivers.
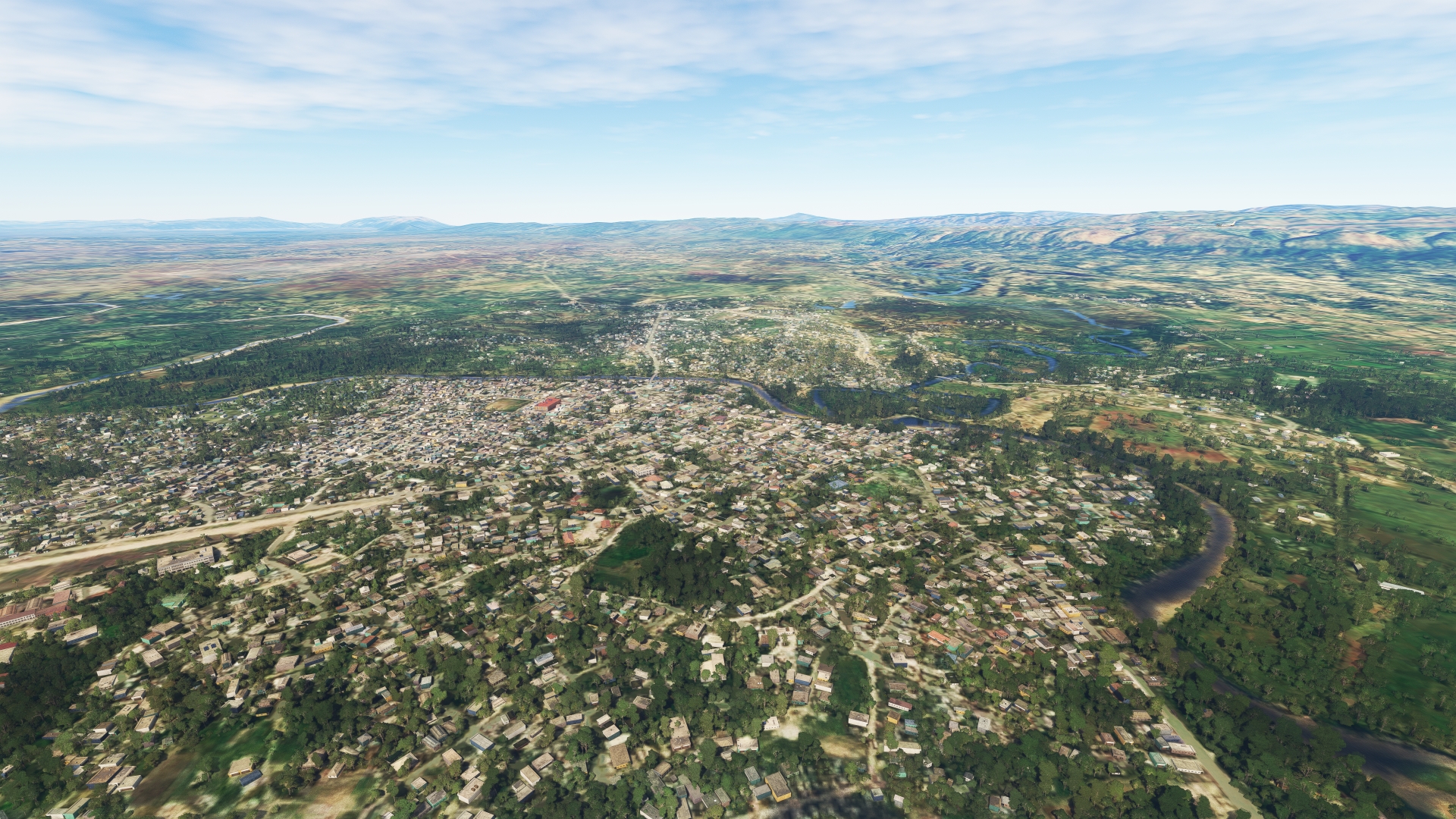
Hinche(POI11) to Pignon(POI12)
Distance: 13.15NM Bearing: 343° 6 minutes
Continue following National Route 3 to the northwest, flying over forested low mountains. Pass over the town of Pignon, located where National Route 3 crosses the Gouape River (Rivière Gouape). After colonization by the French, Pignon and the surrounding valleys became major producers of tobacco, coffee, bananas, and sugar cane. Today, the Pignon region is one of Haiti’s leading sugar cane producers.

Pignon(POI12) to Saint-Raphaël(POI13)
Distance: 7.95NM Bearing: 332° 4 minutes
Parallel National Route 3 to the northeast, remaining to its west. Pass over the mountain village of Saint-Raphaël, located where National Route 3 intersects the Bouyaha River (Rivière Bouyaha). Saint-Raphaël, established in the mid-1700s by colonists from the Canary Islands, today is a major producer of bitter oranges used as the bases for French liqueurs.

Saint-Raphaël(POI13) to Dondon(POI14)
Distance: 5.79NM Bearing: 348° 3 minutes
Parallel the courses of National Route 3 and the Bouyaha River to the mountain town of Dondon. Dondon is renowned throughout the world for its nearby caves, many of which were used by the native Taíno people. The most famous of these caves is the Voûte-à-Minguet, in which the Taíno created petroglyphs. Today the cave is used for ceremonies of Haitian Vodou, which is a synthesis of West and Central African religions and Roman Catholicism that was developed in Haiti beginning in the 16th century.
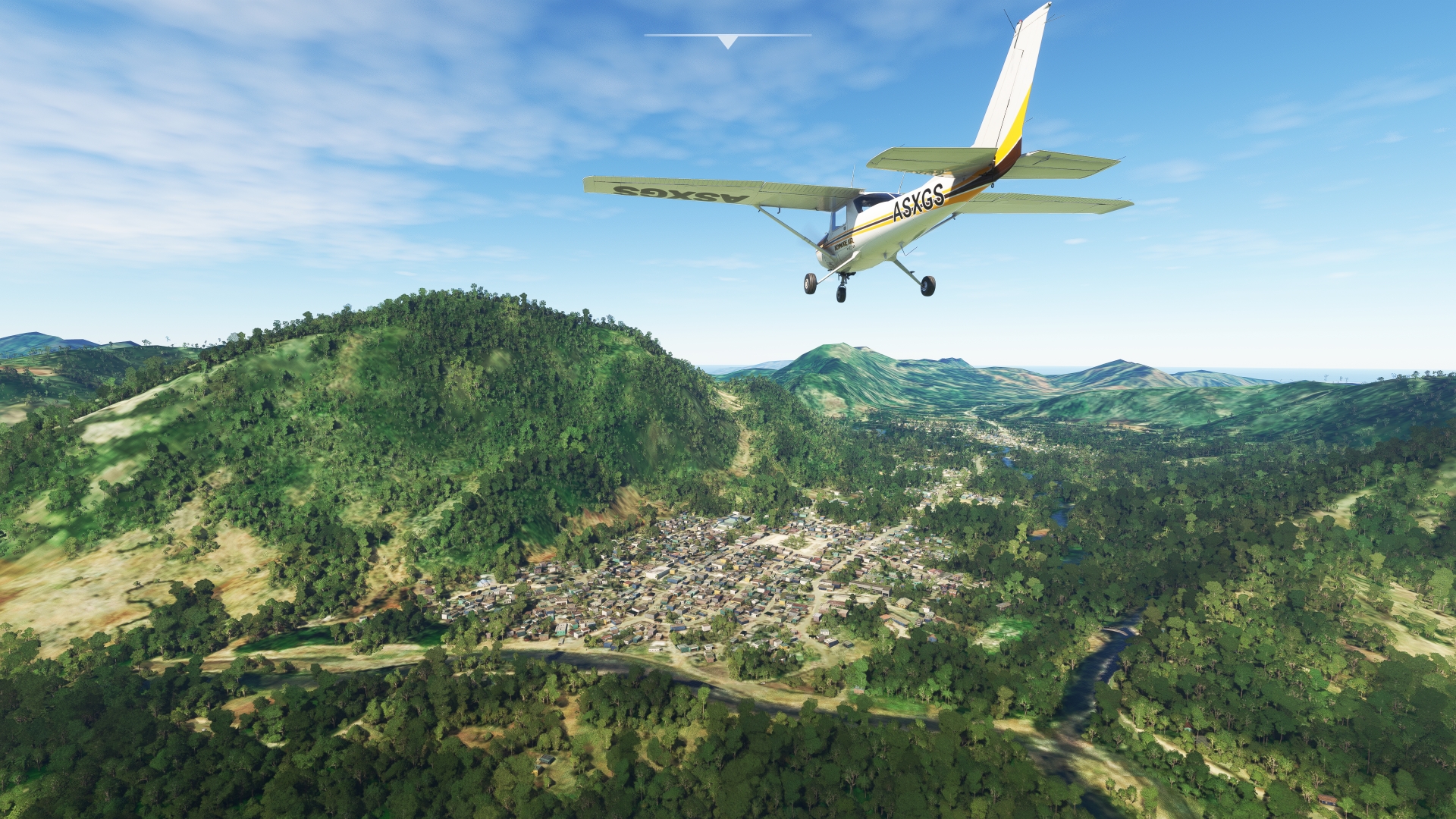

Dondon(POI14) to Milot(MILOT)
Distance: 5.19NM Bearing: 29° 2 minutes
Turn onto a north-northeast heading over Dondon and begin paralleling the course of National Route 3. This section of the flight passes over one of Haiti’s most renowned destinations, National History Park – Citadel, Sans Souci, Ramiers (Parc national historique Citadelle Sans-Souci Ramiers). A UNESCO World Heritage Site, the park protects a number of culturally significant buildings and monuments from Haiti’s independence movement. Maintain course, remaining to the west of National Route 3 and pass over the mountain town of Milot. Milot is the location of Palace of Sans-Souci (Palais Sans Souci), what many Haitians consider to be the most important structure in Haitian society. The palace was one of the first buildings constructed in a liberated Haiti after the Haitian Revolution (1791 to 1804). It was home to Henri Christophe, one of the primary leaders of the revolution and the sole ruler of the Kingdom of Haiti, a monarchy that lasted from 1811 to 1820.

Milot(MILOT) to Cap Haitien Intl(MTCH)
Distance: 7.52NM Bearing: 19° 4 minutes
From Milot, set a course just east of due north and gain a visual on Bay of Cap‑Haïtien (Baie du Cap-Haïtien), which opens to the North Atlantic Ocean. The city of Cap-Haïtien, located just inland of the bay, is one of the most historically significant cities in Haiti as it was the capital of the Kingdom of Haiti (1811 to 1820). Cap-Haïtien International Airport lies due south of Bay of Cap‑Haïtien. Land at the single-runway facility to bring this section of the trip to a close.
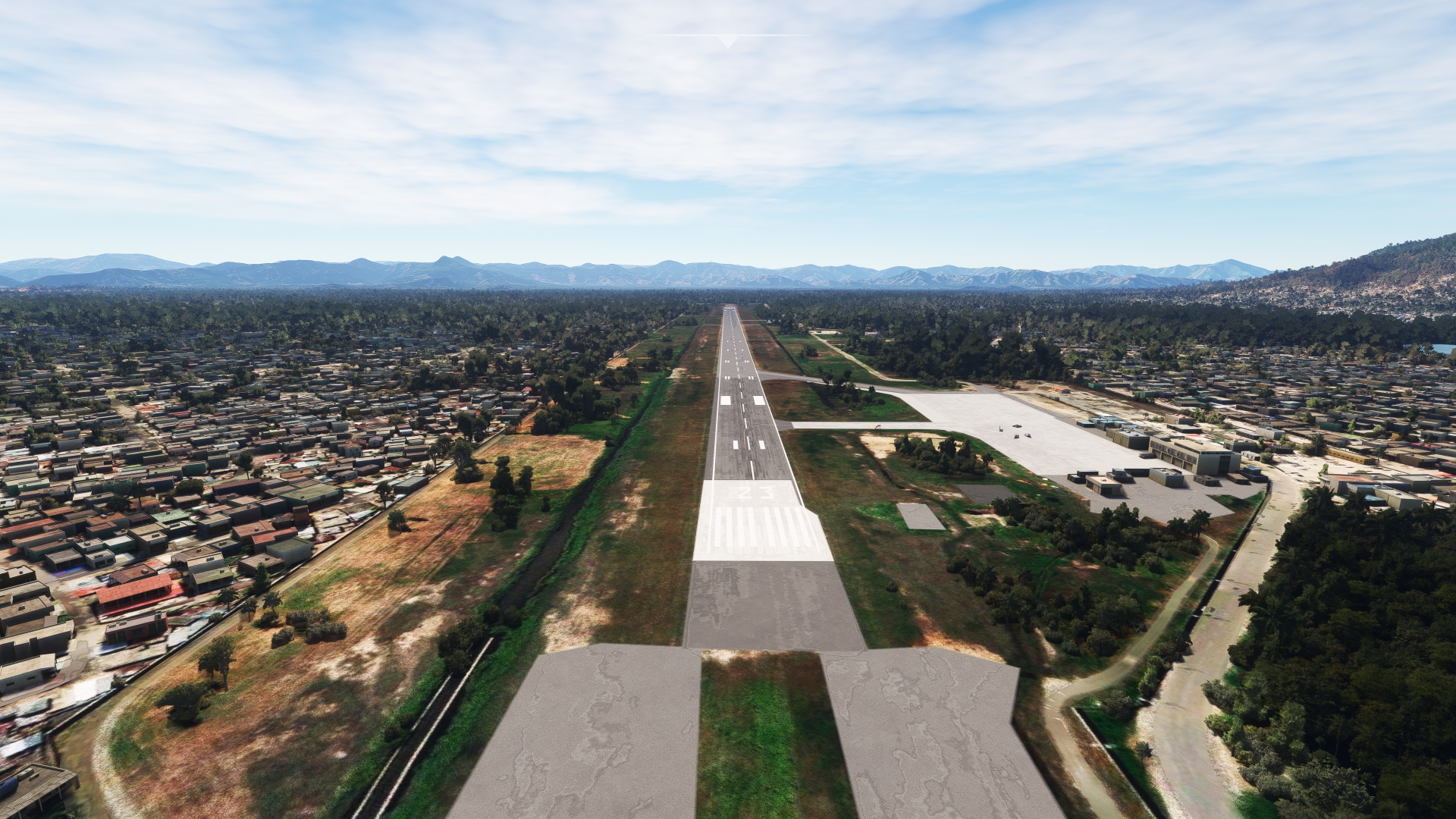

Leg 3
Cap Haitien Intl to Cibao Intl
Leg Distance: 92.61 Approximate time at 125kts: 44 minutes.
Cap Haitien Intl(MTCH) to Fort-Liberté Bay(POI15)
Distance: 18.9NM Bearing: 111° 9 minutes
After lifting off from Cap-Haïtien International Airport, set a course to the east-southeast and pass over Caracol Bay (Baie de Caracol) to reach Fort-Liberté Bay (Baie de Fort-Liberté). The city of Fort-Liberté, which lies just inland of Fort-Liberté Bay, was the location of the declaration of Haitian independence on November 29, 1803.

Fort-Liberté Bay(POI15) to Cañongo(POI16)
Distance: 10.29NM Bearing: 121° 5 minutes
Gain a visual on Lagon-aux-Bœufs, a lagoon rich in wildlife that lies just to the east of Fort-Liberté Bay. Pass just to the south of Lagon-aux-Bœufs and sight Laguna Saladilla, a wetland just over the border from Haiti in northern Dominican Republic. Pass over the international border and fly to the south of Laguna Saladilla and then pass over the village of Cañongo, which lies on highway RD-25, south of the town of Colonia Carbonera.

Cañongo(POI16) to Chacuey Lake(POI17)
Distance: 8.16NM Bearing: 108° 4 minutes
Set a heading just south of due east and pass over lightly forested hills that lie just to the north of agriculture fields. Sight Chacuey Lake (Lago de Chacuey), formed by a dam on the Chacuey River, and pass over its midsection.
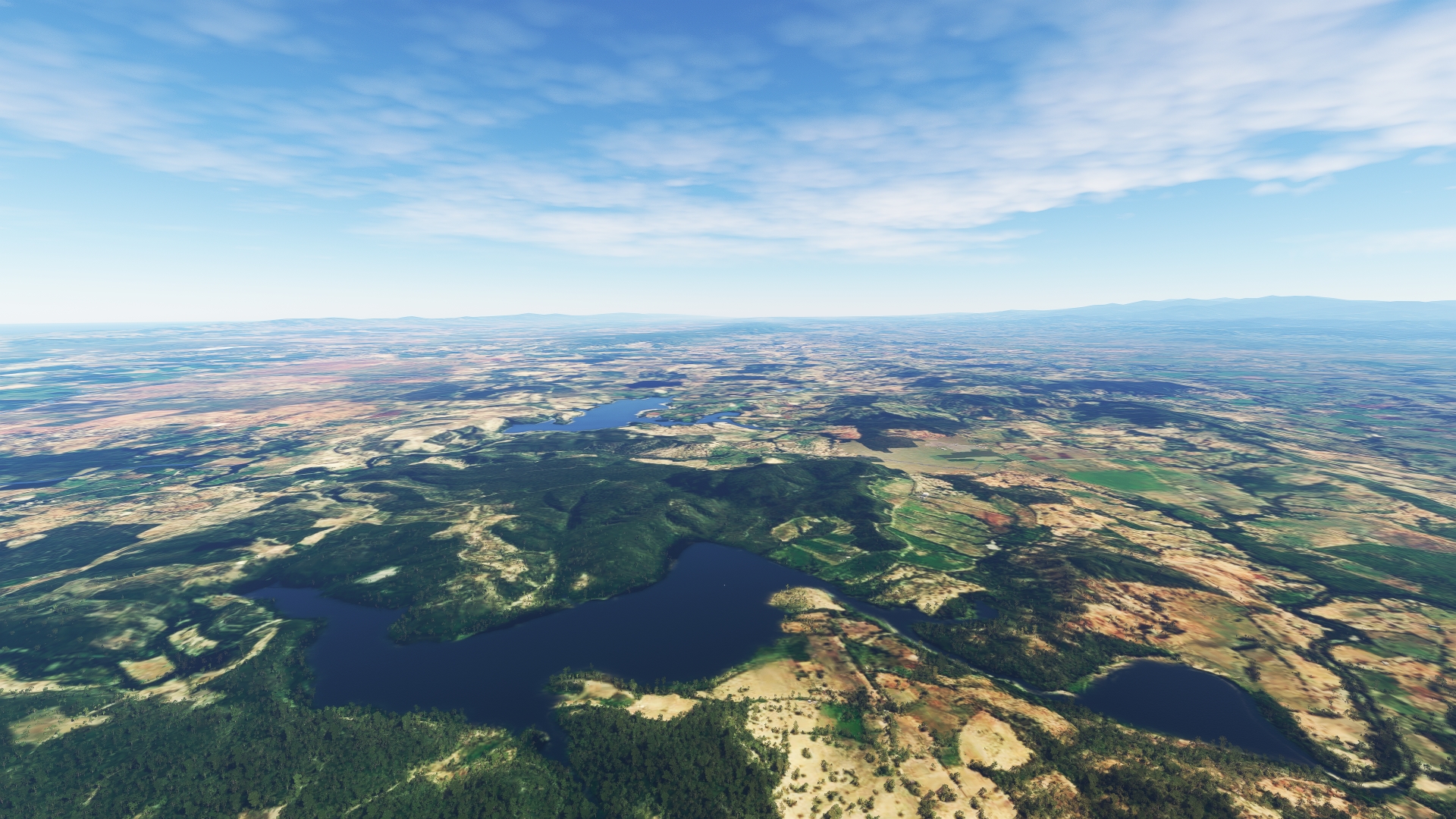

Chacuey Lake(POI17) to Maguaca Lake(POI18)
Distance: 2.6NM Bearing: 95° 1 minutes
Adjust heading slightly to the north and pass over Maguaca Lake (Lago de Maguaca), a reservoir that was formed by the damming of the Maguaca River.

Maguaca Lake(POI18) to Martín García(POI19)
Distance: 6.07NM Bearing: 110° 3 minutes
Change heading slightly to the south to get onto an east-southeast course and pass over the Las Matas Forest Reserve (Reserva Forestal Las Matas). Sight the Guayubín River (Río Guayubín) and highway RD-31 just to its east. Pass over the village of Martín García, which lies along a prominent horseshoe bend in the highway.
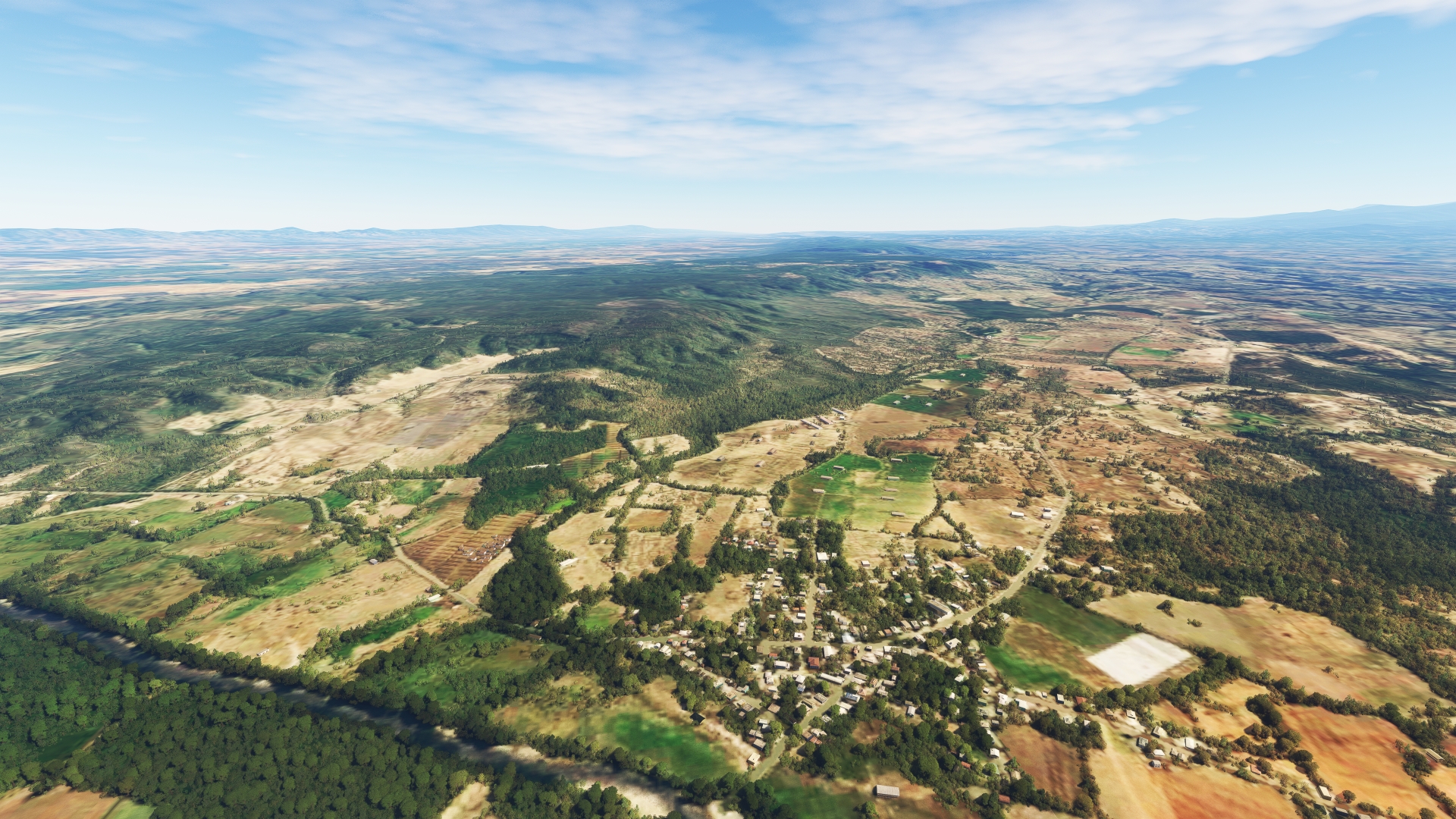

Martín García(POI19) to Mao(MAO)
Distance: 18NM Bearing: 108° 9 minutes
Continue on course and pass over the Río Cana Forest Reserve (Reserva Forestal Río Cana) and the Cana River (Río Cana), which passes through the forested rolling hills of the area. Sight the town of Pueblo Nuevo, which lies on highway RD-20. Pass just to the south of Pueblo Nuevo and parallel RD-20, remaining to its south, to reach the city of Mao. Mao, also called Santa Cruz de Mao, is the largest city in northwestern Dominican Republic and is renowned for its beautiful surroundings and sunsets.

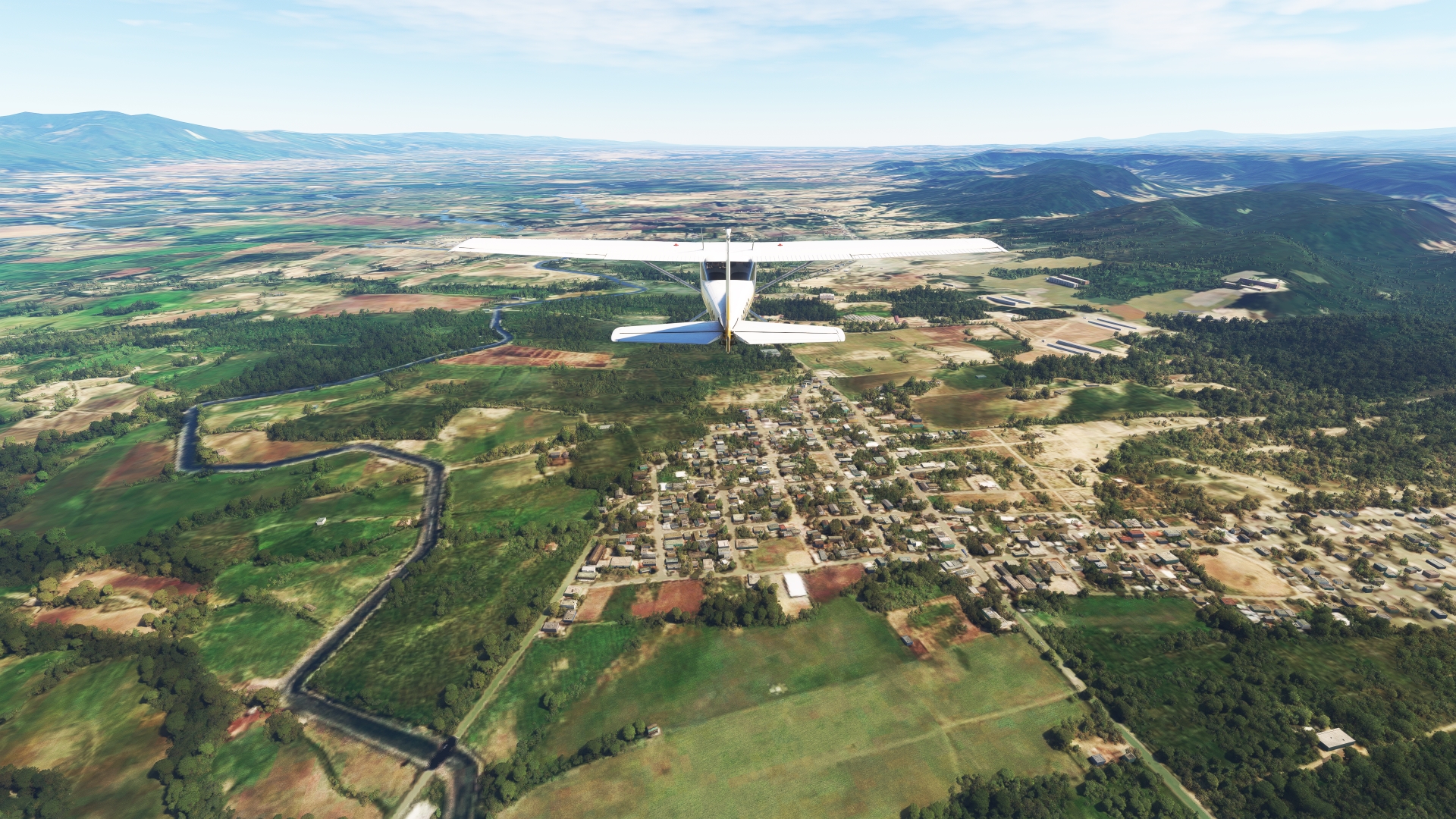
Mao(MAO) to Guatapanal(POI20)
Distance: 9.84NM Bearing: 119° 5 minutes
Adjust course slightly to the south and fly over pastoral scenes of agriculture fields and rolling hills. The hills are the northern limit of the Dominican Republic’s Cordillera Central, the highest mountain range in the country. The range is crowned by Pico Duarte (10,174 feet above sea level), which is the highest mountain in the Dominican Republic, the highest mountain on the island of Hispaniola, and the highest point in the entire Caribbean region. The mountain lies roughly 34 miles to the south of the small town of Guatapanal. The range experiences a wide range of weather through each year, including snow on its highest slopes, due to its altitude. Pass over the Amina River (Río Amina) and then parallel highway RD-18 to reach Guatapanal. This part of the island of Hispaniola was one of the first inland regions to be explored by the Spanish.

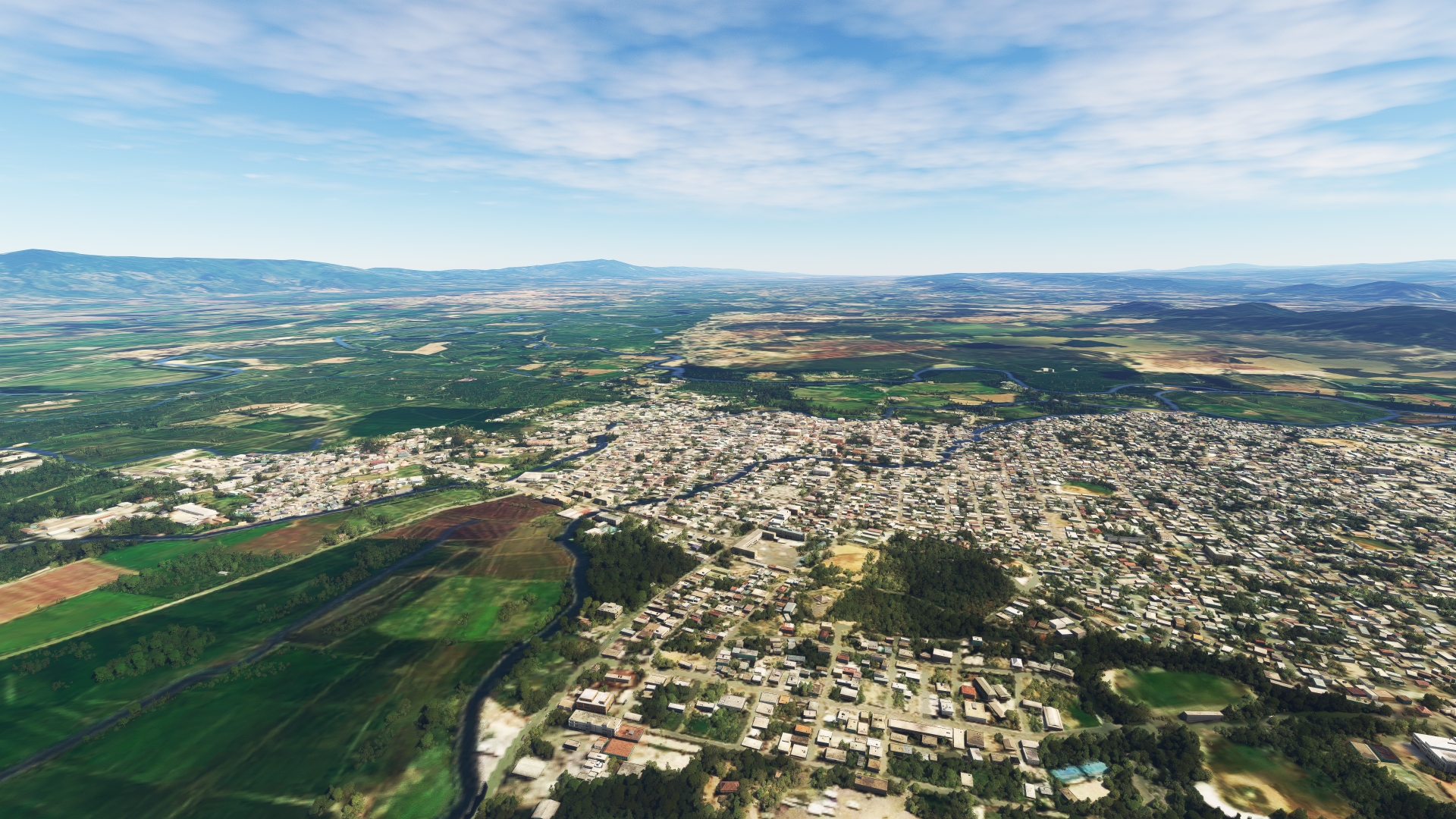
Guatapanal(POI20) to Santiago de los Caballeros(POI21)
Distance: 12.43NM Bearing: 119° 6 minutes
Continue following RD-18 to the city of Santiago de los Caballeros, the second most populous city in the Dominican Republic with over 1.1 million inhabitants. The city, often called “Santiago,” was founded in 1495 and is one of the oldest settlements in the New World. Santiago is located in the Cibao Valley, one of the most agriculturally productive regions in the Dominican Republic. The valley is known for its cigars, livestock, and textiles. Santiago de los Caballeros is today one of the most vibrant economic centers in the Caribbean and is a hub of trade, finance, and light industry.
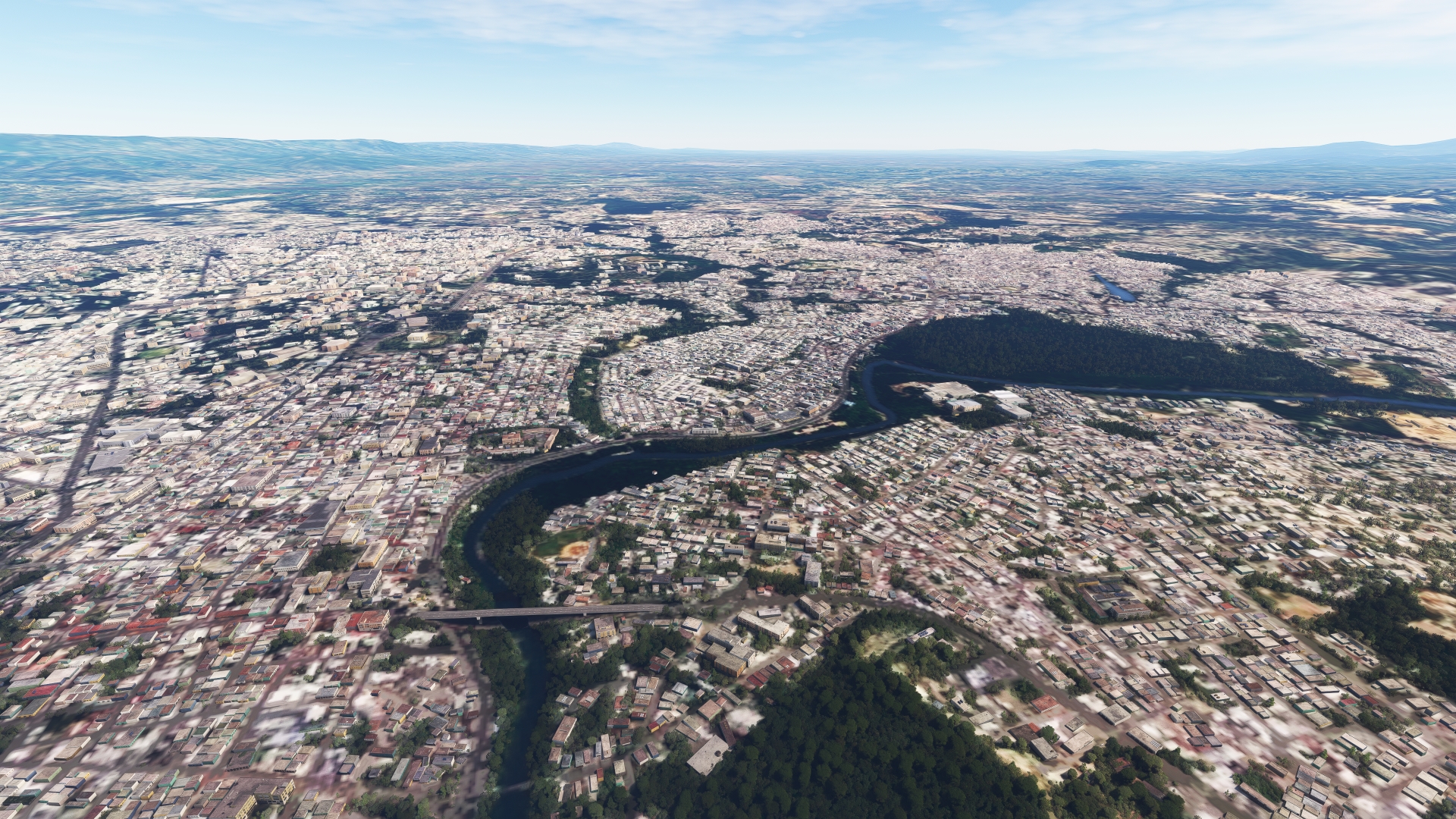

Santiago de los Caballeros(POI21) to Cibao Intl(MDST)
Distance: 6.32NM Bearing: 122° 3 minutes
Continue on course over Santiago de los Caballeros and land at Cibao International Airport.

Leg 4
Cibao Intl to El Catey Intl
Leg Distance: 53.55 Approximate time at 125kts: 26 minutes.
Cibao Intl(MDST) to Tenares(POI22)
Distance: 14.62NM Bearing: 108° 7 minutes
After lifting into the sky at Cibao International Airport, gain a visual on the city of Moca, which lies directly to the east of Santiago de los Caballeros. Moca, the capital of the Dominican Republic’s Espaillat Province, is a city known as the “Village of Heroes” due to a large number of men and women from the area who participated in national conflicts against oppressive regimes. Pass over Moca and gain a visual on Salcedo, the capital of the country’s Hermanas Mirabal Province. Pass just to the north of Salcedo to reach the town of Tenares.

Tenares(POI22) to San Francisco de Macorís(POI23)
Distance: 5.84NM Bearing: 138° 3 minutes
Over Tenares, turn onto a southeasterly heading and follow the general trend of highway RD-132 to the city of San Francisco de Macorís. The Dominican Republic is one of the world’s leading exporters of cocoa, and the San Francisco de Macorís region produces more than half of the nation’s output of this valuable commodity.

San Francisco de Macorís(POI23) to Castillo(POI24)
Distance: 15.08NM Bearing: 128° 7 minutes
Maintain heading and pass over the small village of La Peña. Merge with the pathway of highway RD-132 and follow it to the town of Castillo.

Castillo(POI24) to Arenosa(POI25)
Distance: 9.39NM Bearing: 109° 5 minutes
From Castillo, follow the course of highway RD-132 to the small village of El Abanico. Gain a visual on the Yuna River (Río Yuna) to the east. At 115 miles long, the Yuna is the second longest river in the Dominican Republic. Originating in the Cordillera Central, the river passes through the Cibao Valley and is responsible for its rich soils due to the sediments it deposited over millions of years. Maintain heading and pass over the town of Arenosa, which lies on the northern bank of the Yuna River.

Arenosa(POI25) to El Catey Intl(MDCY)
Distance: 8.62NM Bearing: 67° 4 minutes
Turn onto a northeast heading and follow highway RD-7 to Samaná El Catey International Airport (also called Predident Juan Bosch International Airport) and land. The airport lies at the northwestern aspect of the Samaná Peninsula, which is home to numerous beaches known for their white sand and crystal clear water.

Leg 5
El Catey Intl to Punta Cana Intl
Leg Distance: 95.36 Approximate time at 125kts: 46 minutes.
El Catey Intl(MDCY) to Las Terrenas(POI26)
Distance: 10.79NM Bearing: 91° 5 minutes
Take-off from Samaná El Catey International Airport and follow highway RD-133 to the east, paralleling the northern coastline of the Samaná Peninsula to the town of Las Terrenas. Las Terrenas, initially a small fishing and farming village, has grown into a major tourist destination in the Dominican Republic due to its beaches.

Las Terrenas(POI26) to Samaná(POI27)
Distance: 13.32NM Bearing: 129° 6 minutes
From Las Terrenas, turn onto a southeast heading and pass over the Sierra de Samaná, the low mountains that form the spine of the Samaná Peninsula. Gain a visual on highway RD-5, which runs along the southern coastline of the peninsula and pass over the town of Samaná. The town, the full name of which is Santa Bárbara de Samaná, is located at the head of a small, protected cove of Samaná Bay.

Samaná(POI27) to Samaná Bay(POI28)
Distance: 7.04NM Bearing: 144° 3 minutes
Continue on a southeasterly heading into Samaná Bay. Each year, from the middle of January to late March, North Atlantic humpback whales arrive in Samaná Bay for the winter. After their time in the long, narrow bay, they embark on their return northward journey to destinations as far as Greenland.

Samaná Bay(POI28) to Miches(POI29)
Distance: 14.08NM Bearing: 139° 7 minutes
Continue on course to the southern shore of Samaná Bay to the town of Miches. Nestled between the sea and mountains, Miches is one of the Dominican Republic’s most isolated locations. Agriculture, including the cultivation of cocoa, rice, and coconuts, is the mainstay of the area’s economy.

Miches(POI29) to Laguna Redonda(POI30)
Distance: 6.1NM Bearing: 88° 3 minutes
Over Miches, turn onto a northeast heading and parallel the coastline to Laguna Redonda, Spanish for “Round Lagoon.” Located just inland of the sea, the lagoon is home to numerous bird species and wetland plants. It lies just to the north of Montaña Redonda, “Round Mountain,” a popular tourist destination due to the 360-degree views afforded of this part of the Dominican Republic.

Laguna Redonda(POI30) to Laguna del Limón(POI31)
Distance: 5.57NM Bearing: 122° 3 minutes
Turn onto an east-southeast heading over Laguna Redonda and visit its neighbor, Laguna del Limón, Lemon Lagoon. The lagoon is a beautiful sanctuary that protects mangroves and a rich variety of bird life.

Laguna del Limón(POI31) to Lagunas de Nisibón(POI32)
Distance: 13.34NM Bearing: 141° 6 minutes
Adjust course slightly to the south at Laguna del Limón and follow highway RD-104, which parallels the coastline, to the town of Lagunas de Nisibón.

Lagunas de Nisibón(POI32) to Playa de Arena Gorda(POI33)
Distance: 12.41NM Bearing: 132° 6 minutes
Continue following the coastline to the southeast and pass over Playa Arena Gorda, known for its clear water and white sand beach.

Playa de Arena Gorda(POI33) to Laguna Bávaro(POI34)
Distance: 8.16NM Bearing: 144° 4 minutes
Track the shoreline to the southeast to Laguna Bávaro, a protected lagoon that is home to mangroves and a wide variety of reptile, amphibian, fish, and bird life.

Laguna Bávaro(POI34) to Punta Cana Intl(MDPC)
Distance: 4.55NM Bearing: 188° 2 minutes
Continue following the coastline to the southeast to land at Punta Cana International Airport, which lies due south of Laguna Bávaro. On approach to the airport, pass Cape Engaño (Cabo Engaño), the easternmost land point of the Dominican Republic and the Island of Hispaniola. Punta Cana International Airport, which serves the resort areas of Punta Cana, is the busiest airport in the Dominican Republic and the second busiest in the Caribbean.
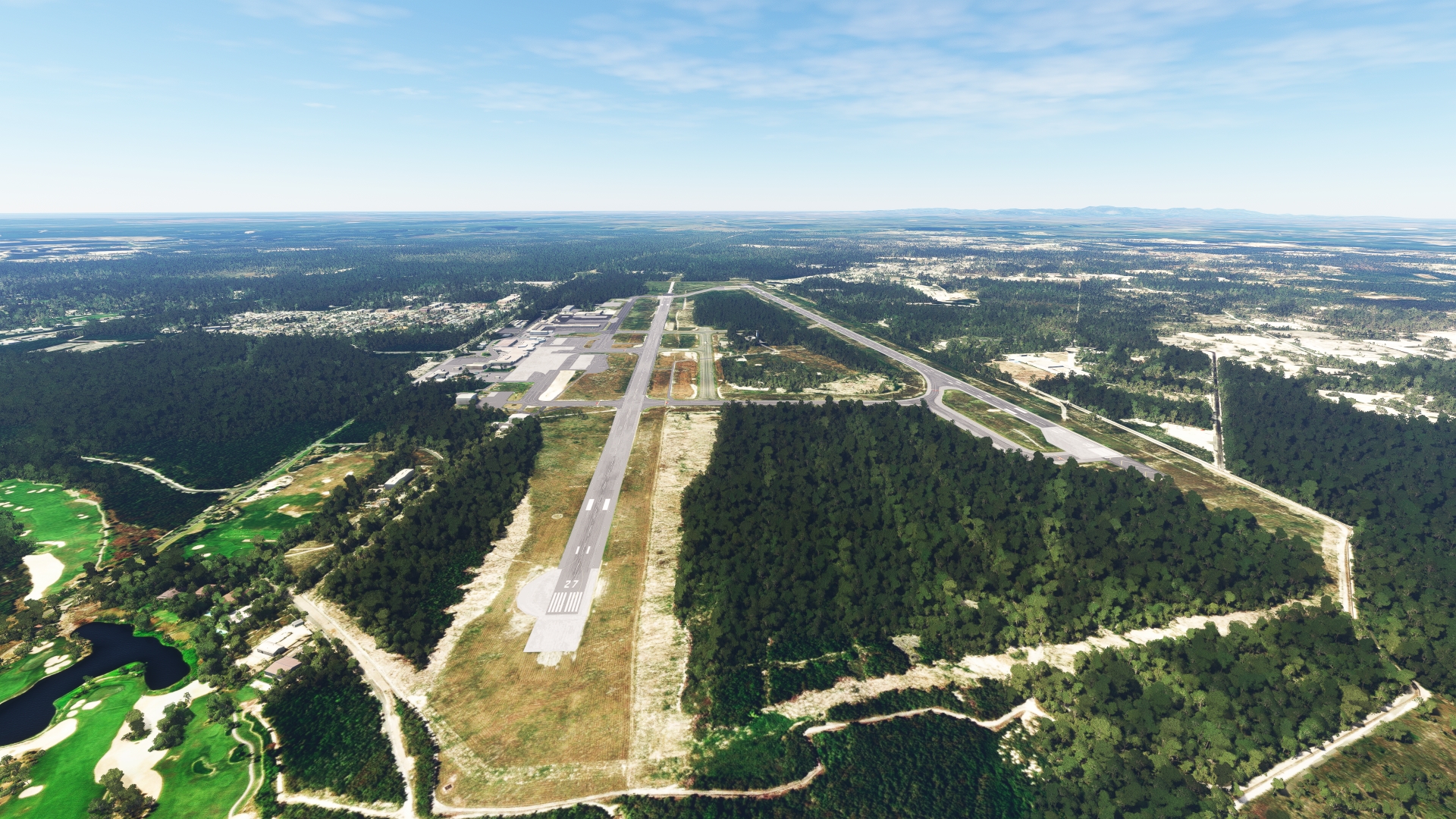

Leg 6
Punta Cana Intl to El Higuero Intl
Leg Distance: 98.45 Approximate time at 125kts: 47 minutes.
Punta Cana Intl(MDPC) to Hoyo Claro Natural Monument(POI35)
Distance: 4.58NM Bearing: 273° 2 minutes
Take-off from Punta Cana International Airport and set a course to the west. Pass over Hoyo Claro Natural Monument (Monumento Natural Hoyo Claro), which protects a cenote, a collapsed cave filled with water.

Hoyo Claro Natural Monument(POI35) to Coral Highway(POI36)
Distance: 21.39NM Bearing: 275° 10 minutes
From Hoyo Claro Natural Monument, continue to the west, paralleling highway RD-3, the “Autopista del Coral,” the Coral Highway. Opened in 2012, the thoroughfare connects the Santo Domingo region with Punta Cana.

Coral Highway(POI36) to Chavón River(POI37)
Distance: 5.26NM Bearing: 237° 3 minutes
Follow the Coral Highway to the west and then to the south. Cross over the Chavón River (Río Chavón) just north of the town of Casa de Campo.

Chavón River(POI37) to La Romana(POI38)
Distance: 5.13NM Bearing: 272° 2 minutes
Continue along the Coral Highway to La Romana. The city, which has its economic roots in sugar and cigars, is today a major Caribbean resort destination.

La Romana(POI38) to San Pedro de Macorís(POI39)
Distance: 19.42NM Bearing: 289° 9 minutes
Continue to the west from La Romana, paralleling the Caribbean coastline, to the city of San Pedro de Macorís. The town was strongly influenced by the influx of Cuban migrants in the 19th century fleeing the Cuban War of Independence.

San Pedro de Macorís(POI39) to Boca Chica(POI40)
Distance: 17.2NM Bearing: 278° 8 minutes
Follow the coastline westward from San Pedro de Macorís to Boca Chica. The city developed around sugar production and then became a resort destination due to its nearby beaches.

Boca Chica(POI40) to Santo Domingo(POI41)
Distance: 19.49NM Bearing: 286° 9 minutes
Continue westward to Santo Domingo, the Dominican Republic’s capital. With 4.5 million inhabitants, Santo Domingo is the most populous city in the Dominican Republic and the entire Caribbean region. The city was founded in the 1490s by Bartholomew Columbus, the brother of Christopher Columbus. Initially named La Nueva Isabela, the settlement was eventually called Santo Domingo, after Saint Dominic (Dominic de Guzmán), the founder of the Dominican Order of the Roman Catholic church. It is the oldest continuously inhabited city of the New World and proved vital to Spanish colonization of the Americas. Today, in addition to being the center of governmental power of the Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo is the nation’s economic, cultural, and educational center.

Santo Domingo(POI41) to El Higuero Intl(MDJB)
Distance: 5.98NM Bearing: 354° 3 minutes
Turn to the northwest and land at La Isabela International Airport, located just to the east of the Isabela River (Río Isabela) on the north side of Santo Domingo.

